Clinical impact of delaying initiation of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with early triple negative breast cancer
- PMID: 38238552
- PMCID: PMC10959785
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-023-07207-4
Clinical impact of delaying initiation of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with early triple negative breast cancer
Abstract
Purpose: The optimal time to initiation of adjuvant chemotherapy (TTAC) for triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients is unclear. This study evaluates the association between TTAC and survival in TNBC patients.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective study using data from a cohort of TNBC patients diagnosed between January 1, 2010 to December 31, 2018, registered in the Tumor Centre Regensburg was conducted. Data included demographics, pathology, treatment, recurrence and survival. TTAC was defined as days from primary surgery to first dose of adjuvant chemotherapy. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to evaluate impact of TTAC on overall survival (OS) and 5-year OS.
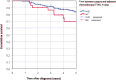
Results: A total of 245 TNBC patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy and valid TTAC data were included. Median TTAC was 29 days. The group receiving systemic therapy within 22 to 28 days after surgery had the most favorable outcome, with median OS of 10.2 years. Groups receiving systemic therapy between 29-35 days, 36-42 days, and more than 6 weeks after surgery had significantly decreased median survival, with median OS of 8.3 years, 7.8 years, and 6.9 years, respectively. Patients receiving therapy between 22-28 days had significantly better survival compared to those receiving therapy between 29-35 days (p = 0.043), and patients receiving therapy after 22-28 days also demonstrated significantly better survival compared to those receiving therapy after more than 43 days (p = 0.033).
Conclusion: Timing of adjuvant systemic therapy can influence OS in TNBC patients. Efforts should be made to avoid unnecessary delays in administering chemotherapy to ensure timely initiation of systemic therapy and optimize patient outcomes.
Keywords: Outcomes in TNBC; Population-based cancer registry; Routine practice data; Timing of adjuvant chemotherapy; Triple negative breast cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Miriam Pigerl, Sophie Räpple, Verena Zeltner, Peter Ugocsai, Elisabeth Inwald, Michael Gerken and Monika Klinkhammer-Schalke declare they have no financial interests. Maria Hatzipanagiotou has received Honoraria for lectures and/or consulting from Novartis, Lilly, Roche, Pfizer and AstraZeneca. Madeleine Hetterich has received speaker honoraria from Celgene, Novartis, MSD, GSK, Eisai and AstraZeneca as well as author honoraria from Thieme and Elsevier and travel reimbursement from Novartis. Olaf Ortmann is on the board of the German Cancer society. He received speaker honoraria from MSD SHARP & DOHME GMBH, Verband Forschender Arzneimittelhersteller vfa, Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, Aurikamed, Med Update, RG Ärztefortbildung, Pierre Fabre Pharma GmbH and holds stocks from Bayer, Novartis, Curevac and Fresenius. Stephan Seitz has received speaker honoraria from AstraZeneca, GE, GSK, IGEA, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and honoraria for consulting from AstraZeneca, GSK, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer and Roche.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does timing of neoadjuvant chemotherapy influence the prognosis in patients with early triple negative breast cancer?J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Oct;149(13):11941-11950. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05060-y. Epub 2023 Jul 7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37418056 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Adjuvant Treatments for T1 N0 M0 Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Nov 2;3(11):e2021881. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.21881. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 33211105 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the Delayed Initiation of Adjuvant Chemotherapy in the Outcome of Triple Negative Breast Cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2021 Jun;21(3):239-246.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2020.09.008. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Clin Breast Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33221201
-
Adjuvant addition of capecitabine to early-stage triple-negative breast cancer patients receiving standard chemotherapy: a meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Feb;179(3):533-542. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05513-4. Epub 2019 Dec 21. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 31865475 Review.
-
Moment of truth-adding carboplatin to neoadjuvant/adjuvant chemotherapy in triple negative breast cancer improves overall survival: An individual participant data and trial-level Meta-analysis.Breast. 2022 Aug;64:7-18. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2022.04.006. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Breast. 2022. PMID: 35462344 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Early death prediction model for breast cancer with synchronous lung metastases: an analysis of the SEER database.Gland Surg. 2024 Oct 31;13(10):1708-1728. doi: 10.21037/gs-24-240. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Gland Surg. 2024. PMID: 39544977 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical outcomes following neoadjuvant chemotherapy with and without immunotherapy in patients with triple-negative breast cancer.Discov Oncol. 2024 Sep 20;15(1):467. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01349-7. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39302495 Free PMC article.
-
Barriers to breast cancer treatment in Brazil: A study on migration and regional disparities.Public Health Pract (Oxf). 2025 May 13;9:100614. doi: 10.1016/j.puhip.2025.100614. eCollection 2025 Jun. Public Health Pract (Oxf). 2025. PMID: 40491549 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Significance of Delays in Initiation of Adjuvant Trastuzumab-Based Therapy in Patients with HER2-Positive Breast Cancer.Biomedicines. 2025 May 26;13(6):1305. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061305. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ortmann O, Blohmer J-U, Sibert NT, Brucker S, Janni W, Wöckel A, et al. Current clinical practice and outcome of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for early breast cancer. Analysis of individual data from 94,638 patients treated in 55 breast cancer centers. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022 doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-03938-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical