Subtypes of nursing students' volunteer motivation in COVID-19: a latent profile analysis
- PMID: 38238711
- PMCID: PMC10797810
- DOI: 10.1186/s12912-024-01699-1
Subtypes of nursing students' volunteer motivation in COVID-19: a latent profile analysis
Abstract
Background: One factor that influences nursing students' decision to engage in volunteer activities is volunteer motivation. It is important to understand the motivations of nursing students to volunteer. However, the majority of current studies have concentrated on the present level of nursing students' motivation to volunteer.
Objectives: To identify subgroups of nursing students' volunteer motivation and its influential factors.
Methods: From January to February 2022, a cross-sectional online study was conducted, and 2569 nursing students from 10 provinces in China were recruited. Participants completed the General Information Questionnaire, Volunteer Functional Inventory (VFI), Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) and Perceived Social Support Scale (PSSS). We explore the categories and characteristics of volunteer motivation using latent profile analysis. Then, we determined factors that affect undergraduate nursing students' volunteer motivation using multinomial logistic regression.
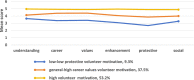
Results: The volunteer motivation score of the nursing students was 77.65 (15.22). The study found that volunteer motivation could be divided into three categories: low-low protective volunteer motivation group (9.3%), general-high career values volunteer motivation group (37.5%), and high volunteer motivation group (53.2%). Perceived social support scale score, perceived stress scale score, gender, and grade significantly influenced the volunteer motivation of nursing students in different categories (both P < 0.05). Women were more likely to have higher motivation to volunteer than men, and fourth-year nursing students were more likely to be in general-high career values volunteer motivation group.
Conclusions: The study highlights the significant heterogeneity in volunteer motivation among nursing students. Higher volunteer motivation was associated with higher perceived social support and lower perceived stress. In addition, gender and academic year were significant influencing factors. Nursing educators should develop targeted volunteer management plans based on the typological characteristics of the population to motivate nursing students to volunteer and promote the development of individual physical and mental health and social well-being.
Trial registration: The survey was approved by the Biomedical Ethics Committee of the Department of Medicine, Xi'an Jiaotong University (No. 2022-0006).
Keywords: Influencing factors; Latent profile analysis; Nursing students; Volunteer motivation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship between benefit finding and volunteer motivation among nursing students: The mediating role of perceived social support.Nurse Educ Today. 2024 Aug;139:106193. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2024.106193. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Nurse Educ Today. 2024. PMID: 38640557
-
Professional calling among nursing students: a latent profile analysis.BMC Nurs. 2023 Sep 2;22(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12912-023-01470-y. BMC Nurs. 2023. PMID: 37660012 Free PMC article.
-
Academic procrastination of nursing students in higher vocational college: Application of latent profile analysis and network analysis.Acta Psychol (Amst). 2024 Jun;246:104296. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2024.104296. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Acta Psychol (Amst). 2024. PMID: 38692067
-
Nursing student volunteerism for marginalized populations: Predictive analysis of influencing factors.Nurse Educ Today. 2025 May;148:106640. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2025.106640. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Nurse Educ Today. 2025. PMID: 40010108
-
Influencing factors of sense of responsibility among undergraduate nursing students: A cross-sectional study.Nurse Educ Today. 2023 Nov;130:105938. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2023.105938. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Nurse Educ Today. 2023. PMID: 37625352
Cited by
-
The influence of credits and stigmas in volunteering on depression, the modulating effects of volunteer personality and motivation.BMC Public Health. 2025 Feb 5;25(1):460. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21727-2. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39910525 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seah B, Ho B, Liaw SY, Ang ENK, Lau ST. To volunteer or not? Perspectives towards pre-registered nursing students volunteering frontline during COVID-19 pandemic to ease healthcare workforce: a qualitative study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:6668. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18126668. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 72104221/National Outstanding Youth Science Fund Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Wjlx2021016/Henan Medical Education Research Program
- Wjlx2021016/Henan Medical Education Research Program
- 21VSZ084/National Social Science Foundation of China Special Project for Research on Civic and Political Science Courses in Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources