The SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway mediates the anti-pulmonary fibrosis effect of liquiritigenin
- PMID: 38238857
- PMCID: PMC10795230
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-024-00886-1
The SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway mediates the anti-pulmonary fibrosis effect of liquiritigenin
Abstract
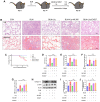
Background: At present, the treatment options available for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis are both limited and often come with severe side effects, emphasizing the pressing requirement for innovative therapeutic alternatives. Myofibroblasts, which hold a central role in pulmonary fibrosis, have a close association with the Smad signaling pathway induced by transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) and the transformation of myofibroblasts driven by oxidative stress. Liquiritigenin, an active compound extracted from the traditional Chinese herb licorice, boasts a wide array of biomedical properties, such as anti-fibrosis and anti-oxidation. The primary objective of this study was to examine the impact of liquiritigenin on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice and the underlying mechanisms.
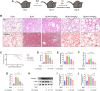
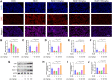
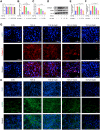
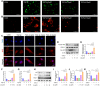
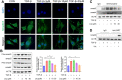
Methods: The anti-pulmonary fibrosis and anti-oxidant effects of liquiritigenin in vivo were tested by HE staining, Masson staining, DHE staining and bio-chemical methods. In vitro, primary mouse lung fibroblasts were treated with TGF-β1 with or without liquiritigenin, the effects of liquiritigenin in inhibiting differentiation of myofibroblasts and facilitating the translocation of Nrf2 were valued using Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (Q-PCR), western blotting and immunofluorescence. Nrf2 siRNA and SIRT1 siRNA were used to investigate the mechanism underlies liquiritigenin's effect in inhibiting myofibroblast differentiation.
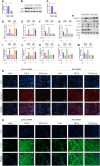
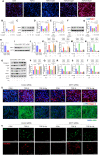
Results: Liquiritigenin displayed a dose-dependent reduction effect in bleomycin-induced fibrosis. In laboratory experiments, it was evident that liquiritigenin possessed the ability to enhance and activate sirtuin1 (SIRT1), thereby facilitating the nuclear translocation of Nrf2 and mitigating the oxidative stress-induced differentiation of primary mouse myofibroblasts. Moreover, our investigation unveiled that SIRT1 not only regulated myofibroblast differentiation via Nrf2-mediated antioxidant responses against oxidative stress but also revealed liquiritigenin's activation of SIRT1, enabling direct binding to Smad. This led to decreased phosphorylation of the Smad complex, constrained nuclear translocation, and suppressed acetylation of the Smad complex, ultimately curtailing the transcription of fibrotic factors. Validation in live subjects provided substantial evidence for the anti-fibrotic efficacy of liquiritigenin through the SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway.
Conclusions: Our findings imply that targeting myofibroblast differentiation via the SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway may constitute a pivotal strategy for liquiritigenin-based therapy against pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords: Liquiritigenin; Myofibroblast differentiation; Nrf2; Oxidative stress; Pulmonary fibrosis; SIRT1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Taraxerone exerts antipulmonary fibrosis effect through Smad signaling pathway and antioxidant stress response in a Sirtuin1-dependent manner.Phytother Res. 2024 Jul;38(7):3720-3735. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8221. Epub 2024 May 22. Phytother Res. 2024. PMID: 38776174
-
Andrographolide ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing cell proliferation and myofibroblast differentiation of fibroblasts via the TGF-β1-mediated Smad-dependent and -independent pathways.Toxicol Lett. 2020 Mar 15;321:103-113. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.11.003. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Toxicol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31706003
-
Nrf2 mediates the effects of shionone on silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis.Chin Med. 2024 Jun 19;19(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00947-5. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38898509 Free PMC article.
-
Pirfenidone attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice by regulating Nrf2/Bach1 equilibrium.BMC Pulm Med. 2017 Apr 18;17(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12890-017-0405-7. BMC Pulm Med. 2017. PMID: 28420366 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3-mediated m6A RNA methylation induces the differentiation of lung resident mesenchymal stem cells into myofibroblasts via the miR-21/PTEN pathway.Respir Res. 2023 Nov 28;24(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02606-z. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 38017523 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical application, potential pharmacological targets and quality marker prediction of a TCM formulation used (Shenling Baizhu San) in the treatment of respiratory diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 29;16:1575903. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1575903. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40510424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating MicroRNAs in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Narrative Review.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Dec 4;46(12):13746-13766. doi: 10.3390/cimb46120821. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39727949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis in pulmonary fibrosis: pathogenesis and traditional Chinese medicine-driven therapeutic approaches.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jul 18;13:1598924. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1598924. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40756260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The chemical composition analysis of Yixin Tongmai Granules using UHPLC-MS/MS and exploration of its potential mechanism in treatment of coronary artery disease based on network pharmacology and molecular docking.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Feb 21;104(8):e41620. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041620. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 39993113 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing Liquiritigenin: A Flavonoid-Based Approach for the Prevention and Treatment of Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 13;17(14):2328. doi: 10.3390/cancers17142328. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723212 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

