Candida auris-associated hospitalizations and outbreaks, China, 2018-2023
- PMID: 38238874
- PMCID: PMC10802803
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2302843
Candida auris-associated hospitalizations and outbreaks, China, 2018-2023
Abstract
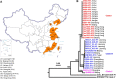
The emerging human fungal pathogen Candida auris has become a serious threat to public health. This pathogen has spread to 10 provinces in China as of December 2023. Here we describe 312 C. auris-associated hospitalizations and 4 outbreaks in healthcare settings in China from 2018 to 2023. Three genetic clades of C. auris have been identified during this period. Molecular epidemiological analyses indicate that C. auris has been introduced and local transmission has occurred in multiple instances in China. Most C. auris isolated from China (98.7%) exhibited resistance to fluconazole, while only a small subset of strains were resistant to amphotericin B (4.2%) and caspofungin (2.2%).
Keywords: Candida auris; China; emerging fungal pathogen; molecular epidemiology; outbreaks.
Conflict of interest statement
Clarissa J. Nobile is a cofounder of BioSynesis, Inc., a company developing diagnostics and therapeutics for biofilm infections.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
