Prognostic Value of BAP1 Protein Expression in Uveal Melanoma
- PMID: 38238977
- PMCID: PMC10876168
- DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000002176
Prognostic Value of BAP1 Protein Expression in Uveal Melanoma
Abstract
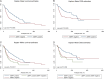
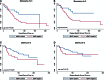
The prognostic value of the traditional pathologic parameters that form part of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system and genetic classifications using monosomy chromosome 3 and structural alterations in chromosome 8 are well established and are part of the diagnostic workup of uveal melanoma (UM). However, it has not been fully clarified whether nuclear protein expression of the tumor suppressor gene BAP1 (nBAP1) by immunohistochemistry alone is as powerful a predictor of overall survival (OS) and/or disease-specific survival (DSS) as chromosome analysis. The protein expression of nBAP1 was evaluated in a retrospective cohort study of 308 consecutive patients treated by primary enucleation between January 1974 and December 2022. We correlated clinical, pathologic, and cytogenetic characteristics to identify the best prognostic indicators for OS and DSS. Loss of nBAP1 was detected in 144/308 (47%) of patients. Loss of nBAP1 expression was significantly associated with poor survival. In patients with disomy chromosome 3, nBAP1 negative is significantly associated with poorer OS but not DSS. We observed that older age (>63 years), presence of metastasis, and nBAP1 negative remained independent prognostic factors in multivariate analysis. nBAP1 protein expression proved to be a more reliable prognostic indicator for OS than the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging, M3 status, or The Cancer Genome Atlas classification in this cohort. This study provides support for accurate prognostication of UM patients in routine histology laboratories by immunohistochemistry for nBAP1 alone.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest and Source of Funding: The authors have disclosed that they have no significant relationships with, or financial interest in, any commercial companies pertaining to this article.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

