Nitro-sulfinate Reductive Coupling to Access (Hetero)aryl Sulfonamides
- PMID: 38239107
- PMCID: PMC10845164
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.3c02557
Nitro-sulfinate Reductive Coupling to Access (Hetero)aryl Sulfonamides
Abstract
A method to assemble (hetero)aryl sulfonamides via the reductive coupling of aryl sulfinates and nitroarenes is reported. Various reducing conditions with sodium bisulfite and with or without tin(II) chloride in DMSO were developed using an ultrasound bath to improve reaction homogeneity and mixing. A range of (hetero)aryl sulfonamides bearing a selection of functional groups were prepared, and the mechanism of the transformation was investigated. These investigations have led us to propose the formation of nitrosoarene intermediates, which were established via an independent molecular coupling strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): The authors declare no competing financial interest(s) other than WJ, PM, ELF and DCB are employees and stockholders of Pfizer Inc.
Figures
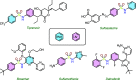


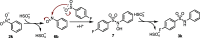
Similar articles
-
Reductant-Free Cross-Electrophile Synthesis of Di(hetero)arylmethanes by Palladium-Catalyzed Desulfinative C-C Coupling.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022 May 2;61(19):e202116775. doi: 10.1002/anie.202116775. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022. PMID: 35229419 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Studies of the Palladium-Catalyzed Desulfinative Cross-Coupling of Aryl Bromides and (Hetero)Aryl Sulfinate Salts.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Feb 19;142(7):3564-3576. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b13260. Epub 2020 Feb 7. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 32031375 Free PMC article.
-
Amine synthesis via iron-catalysed reductive coupling of nitroarenes with alkyl halides.Nat Commun. 2016 Aug 12;7:12494. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12494. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27515391 Free PMC article.
-
Direct sulfonamidation of (hetero)aromatic C-H bonds with sulfonyl azides: a novel and efficient route to N-(hetero)aryl sulfonamides.RSC Adv. 2020 Oct 8;10(61):37299-37313. doi: 10.1039/d0ra04255b. eCollection 2020 Oct 7. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35521237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrophilic halogenation-reductive elimination chemistry of organopalladium and -platinum complexes.Acc Chem Res. 2015 Feb 17;48(2):238-47. doi: 10.1021/ar500325x. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Acc Chem Res. 2015. PMID: 25602260 Review.
Cited by
-
Metal-free introduction of primary sulfonamide into electron-rich aromatics.Chem Sci. 2024 Jul 5;15(31):12310-12315. doi: 10.1039/d4sc03075c. eCollection 2024 Aug 7. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39118614 Free PMC article.
-
Based on magnetically recoverable catalysts: a green strategy to sulfonamides.Mol Divers. 2024 Nov 4. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-11030-4. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2024. PMID: 39495448 Review.
-
Magnetically recoverable catalysts for efficient multicomponent synthesis of organosulfur compounds.RSC Adv. 2025 Feb 6;15(5):3928-3953. doi: 10.1039/d4ra08769k. eCollection 2025 Jan 29. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 39917045 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smith D. A.; Jones R. M. The sulfonamide group as a structural alert: A distorted story?. Curr. Opin. Drug Discovery Devel. 2008, 11, 72–79. - PubMed
- Scott K. A.; Njardarson J. T. Analysis of US FDA-Approved Drugs Containing Sulfur Atoms. Top. Curr. Chem. (Z) 2018, 376, 5.10.1007/s41061-018-0184-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhao C.; Rakesh K. P.; Ravidar L.; Fang W.-Y.; Qin H.-L. Pharmaceutical and medicinal significance of sulfur (SVI)-Containing motifs for drug discovery: A critical review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 162, 679–734. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.11.017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Kalgutkar A. S.; Jones R.; Sawant A. in Metabolism, Pharmacokinetics and Toxicity of Functional Groups: Impact of the Building Blocks of Medicinal Chemistry on ADMET; Smith D. A., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2010, 210 – 274.
-
-
For examples of multicomponent reactions, see:
- DeBergh J. R.; Niljianskul N.; Buchwald S. L. Synthesis of Aryl Sulfonamides via Palladium-Catalyzed Chlorosulfonylation of Arylboronic Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10638–10641. 10.1021/ja405949a. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Chen Y.; Murray P. R. D.; Davies A. T.; Willis M. C. Direct Copper-Catalyzed Three-Component Synthesis of Sulfonamides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 8781–8787. 10.1021/jacs.8b04532. - DOI - PubMed
- Bajohr J.; Diallo A. G.; Whyte A.; Gaillard S.; Renaud J.-L.; Lautens M. Palladium-Catalyzed Domino Heck/Sulfination: Synthesis of Sulfonylated Hetero- and Carbocyclic Scaffolds Using DABCO-Bis(sulfur dioxide). Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 2797–2801. 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c00716. - DOI - PubMed
- Pedersen P. S.; Blakemore D. C.; Chinigo G. M.; Knauber T.; MacMillan D. W. C. One-Pot Synthesis of Sulfonamides from Unactivated Acids and Amines via Aromatic Decarboxylative Halosulfonylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 21189–21196. 10.1021/jacs.3c08218. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Zhang M.; Liu L.; Wang B.; Yang Y.; Liu Y.; Wang Z.; Wang Q. Direct Synthesis of Sulfonamides via Synergetic Photoredox and Copper Catalysis. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 11580–11588. 10.1021/acscatal.3c03096. - DOI
-
For examples of S-N bond formation towards sulfonamides, see:
- Caddick S.; Wilden J. D.; Judd D. B. Direct Synthesis of Sulfonamides and Activated Sulfonate Esters from Sulfonic Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 1024–1025. 10.1021/ja0397658. - DOI - PubMed
- Wright S. W.; Hallstrom K. N. A Convenient Preparation of Heteroaryl Sulfonamides and Sulfonyl Fluorides from Heteroaryl Thiols. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 1080–1084. 10.1021/jo052164+. - DOI - PubMed
- Bahrami K.; Khodaei M. M.; Soheilizad M. Direct Conversion of Thiols to Sulfonyl Chlorides and Sulfonamides. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 9287–9291. 10.1021/jo901924m. - DOI - PubMed
- Taniguchi N. Copper-Catalyzed Formation of Sulfur-Nitrogen Bonds by Dehydrocoupling of Thiols with Amines. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 2010, 2670–2673. 10.1002/ejoc.201000167. - DOI
- Tang X.; Huang L.; Qi C.; Wu X.; Wu W.; Jiang H. Copper-catalyzed sulfonamides formation from sodium sulfinates and amines. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6102–6104. 10.1039/c3cc41249k. - DOI - PubMed
- Pan X.; Gao J.; Liu J.; Lai J.; Jiang H.; Yuan G. Synthesis of sulfonamides via I2-mediated reaction of sodium sulfinates with amines in an aqueous medium at room temperature. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1400–1403. 10.1039/C4GC02115K. - DOI
- Jiang J.; Zeng S.; Chen D.; Cheng C.; Deng W.; Xiang J. Synthesis of N-arylsulfonamides via Fe-promoted reaction of sulfonyl halides with nitroarenes in an aqueous medium. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 5016–5020. 10.1039/C8OB01172A. - DOI - PubMed
-
For examples of C-N bond formation towards sulfonamides, see:
- Burton G.; Cao P.; Li G.; Rivero R. Palladium-Catalyzed Intermolecular Coupling of Aryl Chlorides and Sulfonamides under Microwave Irradiation. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 4373–4376. 10.1021/ol035655u. - DOI - PubMed
- Deng W.; Liu L.; Zhang C.; Liu M.; Guo Q.-X. Copper-catalyzed cross-coupling of sulfonamides with aryl iodides and bromides facilitated by amino acid ligands. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 7295–7298. 10.1016/j.tetlet.2005.08.149. - DOI
- Baffoe J.; Hoe M. Y.; Touré B. B. Copper-Mediated N-Heteroarylation of Primary Sulfonamides: Synthesis of Mono-N-heteroaryl Sulfonamides. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1532–1535. 10.1021/ol100263r. - DOI - PubMed
- Rosen B. R.; Ruble J. C.; Beauchamp T. J.; Navarro A. Mild Pd-Catalyzed N-Arylation of Methanesulfonamide and Related Nucleophiles: Avoiding Potentially Genotoxic Reagents and Byproducts. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2564–2567. 10.1021/ol200660s. - DOI - PubMed
- Shekhar S.; Dunn T. B.; Kotecki B. J.; Montavon D. K.; Cullen S. C. A General Method for Palladium-Catalyzed Reactions of Primary Sulfonamides with Aryl Nonaflates. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 4552–4563. 10.1021/jo200443u. - DOI - PubMed
- Zheng Q.-Z.; Liang Y.-F.; Qin C.; Jiao N. Ru(II)-catalyzed intermolecular C-H amidation of weakly coordinating ketones. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5654–5656. 10.1039/c3cc42613k. - DOI - PubMed
- Bhanuchandra M.; Yadav M. R.; Rit R. K.; Kuram M. R.; Sahoo A. K. Ru(II)-catalyzed intermolecular ortho-C-H amidation of aromatic ketones with sulfonyl azides. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5225–5227. 10.1039/C3CC41915K. - DOI - PubMed
- Cao X.; Bai Y.; Xie Y.; Deng G.-J. Palladium-catalyzed arylation of aryl sulfonamides with cyclohexanones. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2014, 383, 94–100. 10.1016/j.molcata.2013.11.023. - DOI
- Kim T.; McCarver S. J.; Lee C.; MacMillan D. W. C. Sulfonamidation of Aryl and Heteroaryl Halides through Photosensitized Nickel Catalysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3488–3492. 10.1002/anie.201800699. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
For reviews, see:
- Anderson K. K.Comprehensive Organic Chemistry; Pergamon Press: Oxford, 1979, 331– 350;.
- Das T. C.; Quadri S. A.; Farooqui M. Recent advances in synthesis of sulfonamides: A review. J. Chem. Biol. Interfaces 2018, 8, 194–204.
- Mulina O. M.; Ilovaisky A. I.; Terent’ev A. O. Oxidative Coupling with S-N Bond Formation. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 2018, 4648–4672. 10.1002/ejoc.201800838. - DOI
- Joseph D.; Idris M. A.; Chen J.; Lee S. Recent Advances in the Catalytic Synthesis of Arylsulfonyl Compounds. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 4169–4204. 10.1021/acscatal.0c05690. - DOI
-
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

