Enhancing voriconazole therapy in liver dysfunction: exploring administration schemes and predictive factors for trough concentration and efficacy
- PMID: 38239188
- PMCID: PMC10794455
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1323755
Enhancing voriconazole therapy in liver dysfunction: exploring administration schemes and predictive factors for trough concentration and efficacy
Abstract
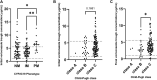
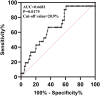
Introduction: The application of voriconazole in patients with liver dysfunction lacks pharmacokinetic data. In previous study, we proposed to develop voriconazole dosing regimens for these patients according to their total bilirubin, but the regimens are based on Monte Carlo simulation and has not been further verified in clinical practice. Besides, there are few reported factors that significantly affect the efficacy of voriconazole. Methods: We collected the information of patients with liver dysfunction hospitalized in our hospital from January 2018 to May 2022 retrospectively, including their baseline information and laboratory data. We mainly evaluated the efficacy of voriconazole and the target attainment of voriconazole trough concentration. Results: A total of 157 patients with liver dysfunction were included, from whom 145 initial and 139 final voriconazole trough concentrations were measured. 60.5% (95/157) of patients experienced the adjustment of dose or frequency. The initial voriconazole trough concentrations were significantly higher than the final (mean, 4.47 versus 3.90 μg/mL, p = 0.0297). Furthermore, daily dose, direct bilirubin, lymphocyte counts and percentage, platelet, blood urea nitrogen and creatinine seven covariates were identified as the factors significantly affect the voriconazole trough concentration. Binary logistic regression analysis revealed that the lymphocyte percentage significantly affected the efficacy of voriconazole (OR 1.138, 95% CI 1.016-1.273), which was further validated by the receiver operating characteristic curve. Conclusion: The significant variation in voriconazole trough concentrations observed in patients with liver dysfunction necessitates caution when prescribing this drug. Clinicians should consider the identified factors, particularly lymphocyte percentage, when dosing voriconazole in this population.
Keywords: efficacy; liver dysfunction; therapeutic drug monitoring; trough concentration; voriconazole.
Copyright © 2024 Zhao, Liu, Xiao, Hou, Zhang, Li, Zhang, Jiang, Sandaradura, Ding and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Population pharmacokinetics, safety and dosing optimization of voriconazole in patients with liver dysfunction: A prospective observational study.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Apr;87(4):1890-1902. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14578. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33010043
-
Therapeutic drug monitoring and safety of voriconazole in elderly patients.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Jan;78:106078. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106078. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31830620
-
Population pharmacokinetic model-guided optimization of intravenous voriconazole dosing regimens in critically ill patients with liver dysfunction.Pharmacotherapy. 2022 Jan;42(1):23-33. doi: 10.1002/phar.2634. Epub 2021 Oct 25. Pharmacotherapy. 2022. PMID: 34655497
-
Voriconazole: a review of adjustment programs guided by therapeutic drug monitoring.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 6;15:1439586. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1439586. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39712496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of CYP2C19 polymorphisms on voriconazole trough concentrations: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Mycoses. 2021 Aug;64(8):860-873. doi: 10.1111/myc.13293. Epub 2021 May 6. Mycoses. 2021. PMID: 33896064
Cited by
-
Therapeutic drug monitoring and safety of voriconazole in patients with liver dysfunction.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 Nov 6;68(11):e0112624. doi: 10.1128/aac.01126-24. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024. PMID: 39431818 Free PMC article.
-
Renal Replacement Therapy as a New Indicator of Voriconazole Clearance in a Population Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Critically Ill Patients.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 22;17(6):665. doi: 10.3390/ph17060665. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brüggemann R. J. M., Alffenaar J.-W. C., Blijlevens N. M. A., Billaud E. M., Kosterink J. G. W., Verweij P. E., et al. (2009). Clinical relevance of the pharmacokinetic interactions of azole antifungal drugs with other coadministered agents. Clin. Infect. Dis. 48 (10), 1441–1458. 10.1086/598327 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

