Plant-derived nanovesicles as an emerging platform for cancer therapy
- PMID: 38239235
- PMCID: PMC10792991
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.08.033
Plant-derived nanovesicles as an emerging platform for cancer therapy
Abstract
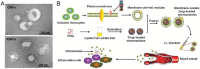
Plant-derived nanovesicles (PDNVs) derived from natural green products have emerged as an attractive nanoplatform in biomedical application. They are usually characterized by unique structural and biological functions, such as the bioactive lipids/proteins/nucleic acids as therapeutics and targeting groups, immune-modulation, and long-term circulation. With the rapid development of nanotechnology, materials, and synthetic chemistry, PDNVs can be engineered with multiple functions for efficient drug delivery and specific killing of diseased cells, which represent an innovative biomaterial with high biocompatibility for fighting against cancer. In this review, we provide an overview of the state-of-the-art studies concerning the development of PDNVs for cancer therapy. The original sources, methods for obtaining PDNVs, composition and structure are introduced systematically. With an emphasis on the featured application, the inherent anticancer properties of PDNVs as well as the strategies in constructing multifunctional PDNVs-based nanomaterials will be discussed in detail. Finally, some scientific issues and technical challenges of PDNVs as promising options in improving anticancer therapy will be discussed, which are expected to promote the further development of PDNVs in clinical translation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures











References
-
- Printezi M.I., Kilgallen A.B., Bond M.J.G., Štibler U., Putker M., Teske A.J., et al. Toxicity and efficacy of chronomodulated chemotherapy: a systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23:e129–e143. - PubMed
-
- Qu Y., Chu B., Wei X., Chen Y., Yang Y., Hu D., et al. Cancer-cell-biomimetic nanoparticles for targeted therapy of multiple myeloma based on bone marrow homing. Adv Mater. 2022;34 - PubMed
-
- Gong L., Zhang Y., Zhao J., Zhang Y., Tu K., Jiao L., et al. All-in-one biomimetic nanoplatform based on hollow polydopamine nanoparticles for synergistically enhanced radiotherapy of colon cancer. Small. 2022;18 - PubMed
-
- Zhang S., Zhang Y., Feng Y., Wu J., Hu Y., Lin L., et al. Biomineralized two-enzyme nanoparticles regulated tumor glycometabolism inducing tumor cell pyroptosis and robust anti-tumor immunotherapy. Adv Mater. 2022;34 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

