Immunomodulatory proteins from hookworms reduce cardiac inflammation and modulate regulatory responses in a mouse model of chronic Trypanosoma cruzi infection
- PMID: 38239430
- PMCID: PMC10795693
- DOI: 10.3389/fpara.2023.1244604
Immunomodulatory proteins from hookworms reduce cardiac inflammation and modulate regulatory responses in a mouse model of chronic Trypanosoma cruzi infection
Abstract
Introduction: Hookworms are parasitic helminths that secrete a variety of proteins that induce anti-inflammatory immune responses, stimulating increased CD4 + Foxp3+ regulatory T cells and IL-10 production. Hookworm-derived recombinant proteins AIP-1 and AIP-2 have been shown to reduce inflammation in mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease and inflammatory airway disease by inducing CD4+Foxp3+ cells and IL-10 production. In contrast, chronic infection with the protozoal parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, the causative agent of Chagas disease, leads to chronic inflammation in tissues. Persistence of the parasites in tissues drives chronic low-grade inflammation, with increased infiltration of inflammatory cells into the heart, accompanied by increased production of inflammatory cytokines. There are no current antiparasitic drugs that effectively reduce or prevent chronic myocarditis caused by the onset of Chagas disease, thus new therapies are urgently needed. Therefore, the impact of AIP-1 and AIP-2 on myocarditis was investigated in a mouse model of chronic T. cruzi infection.
Methods: Female BALB/c mice infected with bioluminescent T. cruzi H1 strain trypomastigotes for 70 days were treated once daily for 7 days with 1mg/kg AIP-1 or AIP-2 protein by intraperitoneal injection. Control mice were left untreated or treated once daily for 14 days with 25mg/kg aspirin in drinking water. At 84 days of infection, splenocytes, cardiac tissue and serum were collected for evaluation.
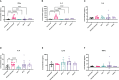
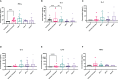
Results: Treatment with both AIP-1 and AIP-2 proteins significantly reduced cardiac cellular infiltration, and reduced cardiac levels of IFNγ, IL-6 and IL-2. AIP-2 treatment reduced cardiac expression of COX-2. Further, while incubation with AIP-1 and AIP-2 proteins did not induce a significant upregulation of an immunoregulatory phenotype in dendritic cells (DC), there was a modest upregulation of CD11c +CD11b+MHCII+SIRPα+ expression, suggesting a regulatory phenotype. Ex-vivo stimulation of splenocytes from the treatment groups with AIP-1 loaded DC induced reduced levels of cytotoxic and pro-inflammatory T cells, stimulation with AIP-2 loaded DC specifically induced enhanced levels of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells among treatment groups.
Discussion: All in vivo and in vitro results demonstrate that hookworm-derived AIP-1 and AIP-2 proteins reduce T. cruzi induced cardiac inflammation, possibly through multiple anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
Keywords: Trypanosoma cruzi; anti-inflammatory; hookworm; immunomodulatory; myocarditis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) VK, WD, BZ and KJ declared that they were editorial board members of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures







Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Population-based interventions for reducing sexually transmitted infections, including HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(2):CD001220. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001220.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Mar 16;(3):CD001220. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001220.pub3. PMID: 15106156 Updated.
Cited by
-
A Honduran Prevalence Study on Soil-Transmitted Helminths Highlights Serological Antibodies to Tm-WAP49 as a Diagnostic Marker for Exposure to Human Trichuriasis.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2025 Feb 11;112(5):1017-1025. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.24-0514. Print 2025 May 7. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2025. PMID: 39933187 Free PMC article.
-
Helminth-derived molecules: Pathogenic and pharmacopeial roles.J Biomed Res. 2024 Sep 24;38(6):547-568. doi: 10.7555/JBR.38.20240177. J Biomed Res. 2024. PMID: 39314046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aliberti J. C., Cardoso M. A., Martins G. A., Gazzinelli R. T., Vieira L. Q., Silva J. S. (1996). Interleukin-12 mediates resistance to Trypanosoma cruzi in mice and is produced by murine macrophages in response to live trypomastigotes. Infect. Immun. 64, 1961–1967. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.6.1961-1967.1996 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

