Mild cognitive impairment prediction and cognitive score regression in the elderly using EEG topological data analysis and machine learning with awareness assessed in affective reminiscent paradigm
- PMID: 38239487
- PMCID: PMC10794306
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1294139
Mild cognitive impairment prediction and cognitive score regression in the elderly using EEG topological data analysis and machine learning with awareness assessed in affective reminiscent paradigm
Abstract
Introduction: The main objective of this study is to evaluate working memory and determine EEG biomarkers that can assist in the field of health neuroscience. Our ultimate goal is to utilize this approach to predict the early signs of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in healthy elderly individuals, which could potentially lead to dementia. The advancements in health neuroscience research have revealed that affective reminiscence stimulation is an effective method for developing EEG-based neuro-biomarkers that can detect the signs of MCI.
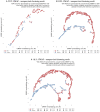
Methods: We use topological data analysis (TDA) on multivariate EEG data to extract features that can be used for unsupervised clustering, subsequent machine learning-based classification, and cognitive score regression. We perform EEG experiments to evaluate conscious awareness in affective reminiscent photography settings.
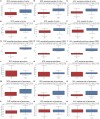
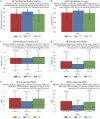
Results: We use EEG and interior photography to distinguish between healthy cognitive aging and MCI. Our clustering UMAP and random forest application accurately predict MCI stage and MoCA scores.
Discussion: Our team has successfully implemented TDA feature extraction, MCI classification, and an initial regression of MoCA scores. However, our study has certain limitations due to a small sample size of only 23 participants and an unbalanced class distribution. To enhance the accuracy and validity of our results, future research should focus on expanding the sample size, ensuring gender balance, and extending the study to a cross-cultural context.
Keywords: EEG; biomarker; machine learning (ML); mild cognitive impairment (MCI); prevention; topological data analysis (TDA).
Copyright © 2024 Rutkowski, Komendziński and Otake-Matsuura.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Bar M. (2022). Mindwandering: How It Can Improve Your Mood and Boost Your Creativity. Bloomsbury Publishing.
-
- Bauer U. (2021). Ripser: efficient computation of Vietoris-Rips persistence barcodes. J. Appl. Comput. Topol. 5, 391–423. 10.1007/s41468-021-00071-5 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

