Potential markers of cancer stem-like cells in ESCC: a review of the current knowledge
- PMID: 38239657
- PMCID: PMC10795532
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1324819
Potential markers of cancer stem-like cells in ESCC: a review of the current knowledge
Abstract
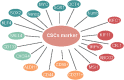
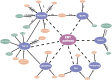
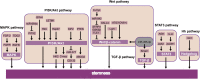
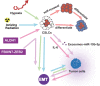
In patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), the incidence and mortality rate of ESCC in our country are also higher than those in the rest of the world. Despite advances in the treatment department method, patient survival rates have not obviously improved, which often leads to treatment obstruction and cancer repeat. ESCC has special cells called cancer stem-like cells (CSLCs) with self-renewal and differentiation ability, which reflect the development process and prognosis of cancer. In this review, we evaluated CSLCs, which are identified from the expression of cell surface markers in ESCC. By inciting EMTs to participate in tumor migration and invasion, stem cells promote tumor redifferentiation. Some factors can inhibit the migration and invasion of ESCC via the EMT-related pathway. We here summarize the research progress on the surface markers of CSLCs, EMT pathway, and the microenvironment in the process of tumor growth. Thus, these data may be more valuable for clinical applications.
Keywords: EMT; cancer stem-like cells; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; microenvironment; surface markers.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Liu, Liu, Guo, Yan, Chen, Wu, Xu, Zhou, Liu, Peng, Cheng and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources