Robotic-assisted sleeve gastrectomy with simultaneous Roux-en-Y cystojejunostomy in a patient with sever obesity and a pancreatic pseudocyst: a case report
- PMID: 38239664
- PMCID: PMC10794364
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2023.1323704
Robotic-assisted sleeve gastrectomy with simultaneous Roux-en-Y cystojejunostomy in a patient with sever obesity and a pancreatic pseudocyst: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: We tried to apply a new surgical method to treat obesity combined with pancreatic pseudocyst and achieved satisfactory results.
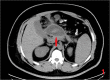
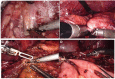
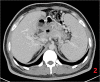
Case and presentation: We report a case of a severely obese patient with pancreatic pseudocyst who underwent robotic-assisted sleeve gastrectomy, while the pseudocyst was incised and cyst-jejunostomy was performed. The operation was successful, and the patient was discharged on the 8th day after the procedure. There were no complications during the perioperative period. After 12 months of follow-up examinations, the patient's pancreatic pseudocyst disappeared. Additionally, there was a significant decrease in body weight, body mass index, and other indicators. As a result, obesity and related metabolic diseases were completely relieved.
Conclusions: This case summarizes and presents the experience of using robotic bariatric surgery for the treatment of pancreatic pseudocyst. This case report indicates that this surgical procedure is both safe and effective for patients with pancreatic pseudocyst who also have obesity and related metabolic diseases.
Keywords: diabete; obesity; pancreatic pseudocyst; robotic surgery; sleeve gastrectomy.
© 2024 Zhang, Wang, Wei, E and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Laparoscopic loop cystojejunostomy: An alternative to Roux-en-Y cystojejunostomy for pancreatic pseudocyst.J Minim Access Surg. 2021 Apr-Jun;17(2):221-225. doi: 10.4103/jmas.JMAS_73_20. J Minim Access Surg. 2021. PMID: 32964880 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of bariatric surgical procedures on the improvement of metabolic syndrome in morbidly obese patients: Comparison of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy versus laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.Turk J Surg. 2017 Sep 1;33(3):142-146. doi: 10.5152/turkjsurg.2017.3865. eCollection 2017. Turk J Surg. 2017. PMID: 28944323 Free PMC article.
-
Robot-assisted sleeve gastrectomy in morbidly obese versus super obese patients.JSLS. 2014 Jul-Sep;18(3):e2014.00099. doi: 10.4293/JSLS.2014.00099. JSLS. 2014. PMID: 25392663 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of weight loss and resolution of comorbidities between laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on 18 studies.Int J Surg. 2020 Apr;76:101-110. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.02.035. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Int J Surg. 2020. PMID: 32151750
-
Candida albicans-infected pancreatic pseudocyst: report of a case.Surg Today. 2004;34(5):466-9. doi: 10.1007/s00595-003-2716-y. Surg Today. 2004. PMID: 15108092 Review.
Cited by
-
Pancreatic Pseudocyst and Obesity: Video Case Report of Management with the One-Stage Procedure.Obes Surg. 2024 Aug;34(8):3097-3104. doi: 10.1007/s11695-024-07335-w. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Obes Surg. 2024. PMID: 38888708
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

