Renewable Syngas Generation via Low-Temperature Electrolysis: Opportunities and Challenges
- PMID: 38239720
- PMCID: PMC10795495
- DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.3c02446
Renewable Syngas Generation via Low-Temperature Electrolysis: Opportunities and Challenges
Abstract
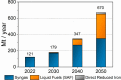
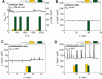
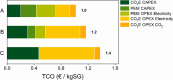
The production of syngas (i.e., a mixture of CO and H2) via the electrochemical reduction of CO2 and water can contribute to the green transition of various industrial sectors. Here we provide a joint academic-industrial perspective on the key technical and economical differences of the concurrent (i.e., CO and H2 are generated in the same electrolyzer cell) and separated (i.e., CO and H2 are electrogenerated in different electrolyzers) production of syngas. Using a combination of literature analysis, experimental data, and techno-economic analysis, we demonstrate that the production of synthesis gas is notably less expensive if we operate a CO2 electrolyzer in a CO-selective mode and combine it with a separate PEM electrolyzer for H2 generation. We also conclude that by the further decrease of the cost of renewable electricity and the increase of CO2 emission taxes, such prepared renewable syngas will become cost competitive.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): eChemicles is scaling up its patented CO2 electrolyzer technology to provide an environmentally and economically sustainable alternative to fossil fuel-based chemicals. Air Liquide offers and operates large-scale PEM water electrolysis solutions for the production of low-carbon hydrogen.
Figures



References
-
- Bolívar Caballero J. J.; Zaini I. N.; Yang W. Reforming Processes for Syngas Production: A Mini-Review on the Current Status, Challenges, and Prospects for Biomass Conversion to Fuels. Applications in Energy and Combustion Science 2022, 10, 100064.10.1016/j.jaecs.2022.100064. - DOI
-
- Wilhelm D. J.; Simbeck D. R.; Karp A. D.; Dickenson R. L. Syngas Production for Gas-to-Liquids Applications: Technologies, Issues and Outlook. Fuel Process. Technol. 2001, 71 (1–3), 139–148. 10.1016/S0378-3820(01)00140-0. - DOI
-
- Bertau M.; Offermanns H.; Plass L.; Schmidt F.; Wernickez H.-J.. Methanol: The Basic Chemical and Energy Feedstock of the Future; Springer: Heidelberg, 2014.
-
- de Klerk A.Fischer–Tropsch Refining; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2011.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
