Pharmacokinetics of florfenicol and its metabolite florfenicol amine in the plasma, urine, and feces of fattening male donkeys following single oral administration
- PMID: 38239747
- PMCID: PMC10794771
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1314029
Pharmacokinetics of florfenicol and its metabolite florfenicol amine in the plasma, urine, and feces of fattening male donkeys following single oral administration
Abstract
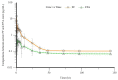
Florfenicol (FF) is a commonly used antibacterial agent in animals. We investigated the pharmacokinetics of FF and its metabolite florfenicol amine (FFA) in donkeys. Donkeys were administered FF (30 mg/kg bodyweight, p.o.). Pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated using a non-compartmental model. The FF (FFA) pharmacokinetics parameters were characterized by along elimination half-life (t1/2 kz) of 5.92 h (15.95 h), plasma peak concentration (Cmax) of 0.13 μg/mL (0.08 μg/mL), and the time taken to reach Cmax (Tmax) of 0.68 h (0.72 h). The area under plasma concentration-time curve and mean residence time of FF (FFA) in plasma were 1.31 μg·mL-1·h (0.47 μg·mL-1·h) and 10.37 h (18.40 h), respectively. The t1/2 kz of FF and FFA in urine was 21.93 and 40.26 h, and the maximum excretion rate was 10.56 and 4.03 μg/h reached at 25.60 and 32.20 h, respectively. The respective values in feces were 0.02 and 0.01 μg·h-1 reached at 33.40 h. The amount of FF and FFA recovered in feces was 0.52 and 0.22 μg, respectively. In conclusion, FF (FFA) is rapidly absorbed and slowly eliminated after a single oral administration to donkeys. Compared to FF, FFA was more slowly eliminated. FF (FFA) is mostly excreted through urine.
Keywords: antibiotic; donkey; florfenicol; florfenicol amine; pharmacokinetics; urinary excretion.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Guo, Qu, Dong, Zhao, Fu, Kang, Cheng, Huang, Zhao and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
HQ and JC were employed by Dong-E-E-Jiao Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics of florfenicol and its metabolite, florfenicol amine, in rice field eel (Monopterus albus) after a single-dose intramuscular or oral administration.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Jun;36(3):229-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2885.2012.01413.x. Epub 2012 May 22. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 22616879
-
Pharmacokinetics of florfenicol and its metabolite florfenicol amine in crucian carp (Carassius auratus) at three temperatures after one single intramuscular injection.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Oct;41(5):739-745. doi: 10.1111/jvp.12672. Epub 2018 Jun 12. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29892973
-
Pharmacokinetics of Enrofloxacin in Plasma, Urine, and Feces of Donkey (Equus asinus) after a Single Intragastric Administration.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Apr 12;13(4):355. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13040355. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667031 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics, optimal dosages and withdrawal time of florfenicol in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) after oral administration via medicated feed.J Fish Dis. 2023 Jan;46(1):75-84. doi: 10.1111/jfd.13719. Epub 2022 Sep 30. J Fish Dis. 2023. PMID: 36179060
-
Pharmacokinetics of florfenicol and behaviour of its metabolite florfenicol amine in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) after oral administration.J Fish Dis. 2016 Jul;39(7):833-43. doi: 10.1111/jfd.12416. Epub 2015 Nov 3. J Fish Dis. 2016. PMID: 26525310
Cited by
-
A Green HPLC Approach to Florfenicol Analysis in Pig Urine.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 12;17(4):495. doi: 10.3390/ph17040495. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675455 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

