Erythritol alters phosphotransferase gene expression and inhibits the in vitro growth of Staphylococcus coagulans isolated from canines with pyoderma
- PMID: 38239752
- PMCID: PMC10794667
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1272595
Erythritol alters phosphotransferase gene expression and inhibits the in vitro growth of Staphylococcus coagulans isolated from canines with pyoderma
Abstract
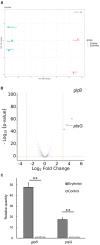
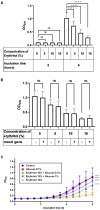
Staphylococcus coagulans (SC) belongs to a group of coagulase-positive staphylococci occasionally isolated from the skin lesions of dogs with pyoderma. We recently revealed that erythritol, a sugar alcohol, inhibited the growth of SC strain JCM7470. This study investigated the molecular mechanisms involved in this growth inhibition of JCM7470 by erythritol, and determine whether erythritol inhibits the growth of SC isolated from the skin of dogs with pyoderma. Comprehensive analysis of the gene expression of JCM7470 in the presence of erythritol revealed that erythritol upregulated the expression of glcB and ptsG genes, both of which encode phosphotransferase system (PTS) glucoside- and glucose-specific permease C, B, and A domains (EIICBA), respectively, associated with sugar uptake. Moreover, erythritol suppressed in vitro growth of all 27 SC strains isolated from the skin lesions of canine pyoderma, including 13 mecA gene-positive and 14 mecA gene-negative strains. Finally, the growth inhibition of the SC clinical isolates by erythritol was restored by the addition of glucose. In summary, we revealed that erythritol promotes PTS gene expression and suppresses the in vitro growth of SC clinical isolates from dogs with pyoderma. Restoration of the erythritol-induced growth inhibition by glucose suggested that glucose starvation may contribute to the growth inhibition of SC.
Keywords: Staphylococcus coagulans; dog; erythritol; glucose; phosphotransferase system; pyoderma.
Copyright © 2024 Onishi-Sakamoto, Fujii, Watanabe, Makida, Iyori, Toyoda, Tochio and Nishifuji.
Conflict of interest statement
RM is an employee of B Food Science Co., Ltd. TF and TT were employees of the same company at the time when this study was started. KI was employed by Vet Derm Tokyo Ltd. where YT the representative director. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Madhaiyan M, Wirth JS, Saravanan VS. Phylogenomic analyses of the Staphylococcaceae family suggest the reclassification of five species within the genus Staphylococcus as heterotypic synonyms, the promotion of five subspecies to novel species, the taxonomic reassignment of five Staphylococcus species to Mammaliicoccus gen. nov, and the formal assignment of Nosocomiicoccus to the family Staphylococcaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. (2020) 70:5926–36. 10.1099/ijsem.0.004498 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

