Prognostic Nutritional Index as a Prognostic Factor for Very Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 38240325
- PMCID: PMC11042774
- DOI: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000678
Prognostic Nutritional Index as a Prognostic Factor for Very Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Introduction: Field factors play more important roles in predicting the outcomes of patients compared with tumor factors in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the prognostic ability of noninvasive serum marker scores for hepatic fibrosis and liver functional reserve on very early-stage HCC is still not yet determined. We aimed to investigate the performance of these serum marker scores in predicting the prognoses of patients with very early-stage HCC.
Methods: A total of 446 patients with very early-stage HCC from 2012 to 2022 were retrospectively enrolled. Serum biomarkers and prognostic scores determining overall survival (OS) were analyzed by Cox proportional hazards model. We compared the Akaike information criterion among the prognostic nutritional index (PNI), aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index, albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) score, EZ (easy)-ALBI score, modified ALBI score, fibrosis-4 score, and lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio to determine the predictability on the OS.
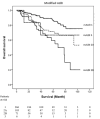
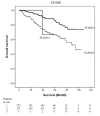
Results: After a median follow-up of 41.0 months (interquartile range 36.9-45.1 months), 81 patients died, with a 5-year OS rate of 71.0%. Among the noninvasive serum marker scores, PNI had the best performance in predicting the OS with the lowest Akaike information criterion (846.407) compared with other scores. Moreover, we stratified the patients into high-risk (PNI <45) and low-risk (PNI ≥45) groups. It showed that the 5-year OS rates were 83.4% and 60.8% in the low-risk and high-risk PNI groups, respectively ( P < 0.001).
Discussion: PNI had the best performance in predicting the OS for patients with very early-stage HCC.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. . Global cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Villanueva A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2019;380(15):1450–62. - PubMed
-
- Chang CY, Wei CY, Chen PH, et al. . The role of albumin-bilirubin grade in determining the outcomes of patients with very early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J Chin Med Assoc 2021;84(2):136–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MOST 111-2314-B-075-056, MSTC 112-2314-B-075-043-MY2/National Science and Technology Council of Taiwan
- (V112C-039, Center of Excellence for Cancer Research MOHW112-TDU-B-221-124007, and Big Data Center), Y.L. Lin Hung Tai Education Foundation, and Yin Shu-Tien Foundation Taipei Veterans General Hospital-National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University Excellent Physician Scientists Cultivation Program, No. 112-V-B-073)./Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- (V112C-039, Center of Excellence for Cancer Research MOHW112-TDU-B-221-124007, and Big Data Center), Y.L. Lin Hung Tai Education Foundation, and Yin Shu-Tien Foundation Taipei Veterans General Hospital-National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University Excellent Physician Scientists Cultivation Program, No. 112-V-B-073)/Taipei Veterans General Hospital
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical