Volume expansion mitigates Shiga toxin-producing E. coli-hemolytic uremic syndrome in children
- PMID: 38240870
- PMCID: PMC11026235
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-023-06276-3
Volume expansion mitigates Shiga toxin-producing E. coli-hemolytic uremic syndrome in children
Abstract
Background: Shiga toxin-producing E. coli-hemolytic uremic syndrome (STEC-HUS) is associated with high morbidity and relevant mortality. Previous small studies showed that volume expansion could improve the course and outcome of STEC-HUS. The aim of this single-center study was to evaluate the effect of volume expansion on the clinical course and outcome in STEC-HUS.
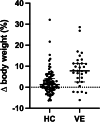
Methods: Data of pediatric patients with STEC-HUS were analyzed retrospectively. Course and outcome of patients treated with volume expansion (VE) from 2019 to 2022 (n = 38) were compared to historical controls (HC) from 2009 to 2018 (n = 111).
Results: Patients in the VE group had a significant relative median weight gain compared to HC (7.8% (3.4-11.3) vs. 1.2% (- 0.7-3.9), p < 0.0001) 48 h after admission. The need for dialysis was not reduced by VE (VE 21/38 (55.3%) vs. HC 64/111 (57.7%), p = 0.8). However, central nervous system involvement (impairment of consciousness, seizures, focal neurological deficits, and/or visual disturbances) was significantly reduced (VE 6/38 (15.8%) vs. HC 38/111 (34.2%), p = 0.039). None of the patients in the VE group died or developed chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage 5, whereas in the HC group, three patients died and three patients had CKD stage 5 at discharge.
Conclusions: This study suggests that volume expansion may be associated with the mitigation of the acute course of STEC-HUS, especially severe neurological involvement and the development of CKD. Prospective trials should lead to standardized protocols for volume expansion in children with STEC-HUS.
Keywords: EHEC; HUS; Hyperhydration; Outcome; STEC; Volume expansion.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Rosales A, Hofer J, Zimmerhackl LB, Jungraithmayr TC, Riedl M, Giner T, Strasak A, Orth-Holler D, Wurzner R, Karch H. Need for long-term follow-up in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome due to late-emerging sequelae. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54:1413–1421. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis196. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Loos S, Aulbert W, Hoppe B, Ahlenstiel-Grunow T, Kranz B, Wahl C, Staude H, Humberg A, Benz K, Krause M, Pohl M, Liebau MC, Schild R, Lemke J, Beringer O, Muller D, Hartel C, Wigger M, Vester U, Konrad M, Haffner D, Pape L, Oh J, Kemper MJ. Intermediate follow-up of pediatric patients with hemolytic uremic syndrome during the 2011 outbreak caused by E. coli O104:H4. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64:1637–1643. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix218. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical