miRNAs in pancreatic cancer progression and metastasis
- PMID: 38240887
- PMCID: PMC11213741
- DOI: 10.1007/s10585-023-10256-0
miRNAs in pancreatic cancer progression and metastasis
Abstract
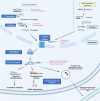
Small non-coding RNA or microRNA (miRNA) are critical regulators of eukaryotic cells. Dysregulation of miRNA expression and function has been linked to a variety of diseases including cancer. They play a complex role in cancers, having both tumour suppressor and promoter properties. In addition, a single miRNA can be involved in regulating several mRNAs or many miRNAs can regulate a single mRNA, therefore assessing these roles is essential to a better understanding in cancer initiation and development. Pancreatic cancer is a leading cause of cancer death worldwide, in part due to the lack of diagnostic tools and limited treatment options. The most common form of pancreatic cancer, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), is characterised by major genetic mutations that drive cancer initiation and progression. The regulation or interaction of miRNAs with these cancer driving mutations suggests a strong link between the two. Understanding this link between miRNA and PDAC progression may give rise to novel treatments or diagnostic tools. This review summarises the role of miRNAs in PDAC, the downstream signalling pathways that they play a role in, how these are being used and studied as therapeutic targets as well as prognostic/diagnostic tools to improve the clinical outcome of PDAC.
Keywords: Diagnostics; Novel therapeutics; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; microRNA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

