Evaluating deep learning-based melanoma classification using immunohistochemistry and routine histology: A three center study
- PMID: 38241314
- PMCID: PMC10798511
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297146
Evaluating deep learning-based melanoma classification using immunohistochemistry and routine histology: A three center study
Abstract
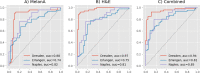
Pathologists routinely use immunohistochemical (IHC)-stained tissue slides against MelanA in addition to hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained slides to improve their accuracy in diagnosing melanomas. The use of diagnostic Deep Learning (DL)-based support systems for automated examination of tissue morphology and cellular composition has been well studied in standard H&E-stained tissue slides. In contrast, there are few studies that analyze IHC slides using DL. Therefore, we investigated the separate and joint performance of ResNets trained on MelanA and corresponding H&E-stained slides. The MelanA classifier achieved an area under receiver operating characteristics curve (AUROC) of 0.82 and 0.74 on out of distribution (OOD)-datasets, similar to the H&E-based benchmark classification of 0.81 and 0.75, respectively. A combined classifier using MelanA and H&E achieved AUROCs of 0.85 and 0.81 on the OOD datasets. DL MelanA-based assistance systems show the same performance as the benchmark H&E classification and may be improved by multi stain classification to assist pathologists in their clinical routine.
Copyright: © 2024 Wies et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
TJB would like to disclose that he is the owner of Smart Health Heidelberg GmbH (Handschuhsheimer Landstr. 9/1, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany) which develops mobile apps, outside of the submitted work. SHo reports clinical trial support from Almirall and speaker’s honoraria from Almirall, UCB and AbbVie and has received travel support from the following companies: UCB, Janssen Cilag, Almirall, Novartis, Lilly, LEO Pharma and AbbVie outside the submitted work. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

