Global oceanic oxygenation controlled by the Southern Ocean through the last deglaciation
- PMID: 38241365
- PMCID: PMC10798564
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adk2506
Global oceanic oxygenation controlled by the Southern Ocean through the last deglaciation
Abstract
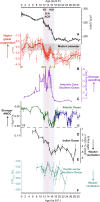
Ocean dissolved oxygen (DO) can provide insights on how the marine carbon cycle affects global climate change. However, the net global DO change and the controlling mechanisms remain uncertain through the last deglaciation. Here, we present a globally integrated DO reconstruction using thallium isotopes, corroborating lower global DO during the Last Glacial Maximum [19 to 23 thousand years before the present (ka B.P.)] relative to the Holocene. During the deglaciation, we reveal reoxygenation in the Heinrich Stadial 1 (~14.7 to 18 ka B.P.) and the Younger Dryas (11.7 to 12.9 ka B.P.), with deoxygenation during the Bølling-Allerød (12.9 to 14.7 ka B.P.). The deglacial DO changes were decoupled from North Atlantic Deep Water formation rates and imply that Southern Ocean ventilation controlled ocean oxygen. The coherence between global DO and atmospheric CO2 on millennial timescales highlights the Southern Ocean's role in deglacial atmospheric CO2 rise.
Figures


References
-
- Jaccard S. L., Galbraith E. D., Martínez-Garciá A., Anderson R. F., Covariation of deep Southern Ocean oxygenation and atmospheric CO2 through the last ice age. Nature 530, 207–210 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Jaccard S. L., Galbraith E. D., Large climate-driven changes of oceanic oxygen concentrations during the last deglaciation. Nat. Geosci. 5, 151–156 (2012).
-
- Jacobel A. W., Anderson R. F., Jaccard S. L., McManus J. F., Pavia F. J., Winckler G., Deep Pacific storage of respired carbon during the last ice age: Perspectives from bottom water oxygen reconstructions. Quat. Sci. Rev. 230, 106065 (2020).
-
- Zhou Y., McManus J. F., Authigenic uranium deposition in the glacial North Atlantic: Implications for changes in oxygenation, carbon storage, and deep water-mass geometry. Quat. Sci. Rev. 300, 107914 (2023).
-
- Deutsch C., Brix H., Ito T., Frenzel H., Thompson L. A., Climate-forced variability of ocean hypoxia. Science 333, 336–339 (2011). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

