Predictive value of serum TBA for 2-year MACEs in ACS patients undergoing PCI: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 38242883
- PMCID: PMC10799034
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-50304-z
Predictive value of serum TBA for 2-year MACEs in ACS patients undergoing PCI: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
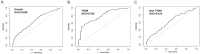
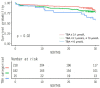
Bile acids play important roles in lipid metabolism and glucose homeostasis. Limited research exist on the association between serum total bile acid (TBA) levels and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS), particularly those with comorbid type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This study was conducted to examine the relationship between baseline serum TBA level and T2DM status in patients with ACS after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and to identify the predictive value of TBA levels for a 2-year risk of MACEs. 425 ACS patients underwent PCI were recruited and divided into three groups based on baseline serum TBA concentration. An analysis of the association between the T2DM status and baseline serum TBA levels was conducted using univariate linear regression and multivariate linear regression. The predictive relevance of serum TBA levels was evaluated using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and Cox regression. Kaplan-Meier curves were employed to analyze the differences among groups in predicting MACEs over a 2-year follow-up period. Baseline serum TBA levels were higher in ACS patients who were diagnosed with T2DM (the median 3.6 µmol/L) than those without T2DM (the median 3.0 µmol/L). T2DM status in ACS patients was positively correlated with baseline serum TBA concentrations (β: 1.7, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.3-3.0), particularly in the male (β: 2.0, 95% CI 0.3-3.6) and 50-69-year-old (β: 2.5, 95% CI 0.6-4.4) populations. The areas under the ROC curve of baseline serum TBA levels predicted MACEs in ACS and ACS-T2DM patients following PCI were 0.649 (95% CI 0.595-0.703) and 0.783 (95% CI 0.685-0.881), respectively. Furthermore, Cox regression analysis showed that baseline serum TBA level was associated with the occurrence of MACEs in patients with ACS after PCI over a 2-year follow-up period, especially in those diagnosed with T2DM, whose baseline TBA concentration was lower than 10.0 µmol/L. ACS Patients with T2DM had higher serum TBA levels. TBA level at baseline was an independent predictor of MACEs in ACS patients who underwent PCI, especially with comorbid T2DM.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Baseline plasma fibrinogen is associated with haemoglobin A1c and 2-year major adverse cardiovascular events following percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a single-centre, prospective cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019 Apr 23;18(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0858-5. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019. PMID: 31014348 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive value of the triglyceride glucose index combined with cystatin C for the prognosis of patients with acute coronary syndrome.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 14;15:1423227. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1423227. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39257901 Free PMC article.
-
A synergistic effect of the triglyceride-glucose index and the residual SYNTAX score on the prediction of intermediate-term major adverse cardiac events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Jun 24;21(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01553-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35751060 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of short-term high-dose atorvastatin pretreatment in patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a meta-analysis of nine randomized controlled trials.Clin Cardiol. 2013 Dec;36(12):E41-8. doi: 10.1002/clc.22198. Epub 2013 Aug 27. Clin Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 24038054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet-To-Lymphocyte Ratio Efficiency in Predicting Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Acute Coronary Syndromes: A Meta-Analysis.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025 May 21;26(5):27942. doi: 10.31083/RCM27942. eCollection 2025 May. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40475740 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
High Starch Induces Hematological Variations, Metabolic Changes, Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory Responses, and Histopathological Lesions in Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides).Metabolites. 2024 Apr 19;14(4):236. doi: 10.3390/metabo14040236. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38668364 Free PMC article.
-
Bile Acids as Emerging Players at the Intersection of Steatotic Liver Disease and Cardiovascular Diseases.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 12;14(7):841. doi: 10.3390/biom14070841. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Time in Target Range of Resting Heart Rate With Adverse Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndromes After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.Glob Heart. 2025 Jan 17;20(1):3. doi: 10.5334/gh.1384. eCollection 2025. Glob Heart. 2025. PMID: 39829969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Luca G, Verdoia M, Suryapranata H. Benefits from intracoronary as compared to intravenous abciximab administration for STEMI patients undergoing primary angioplasty: A meta-analysis of 8 randomized trials. Atherosclerosis. 2012;222:426–433. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.02.041. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

