Bispecific BCMA/CD24 CAR-T cells control multiple myeloma growth
- PMID: 38242888
- PMCID: PMC10798961
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-44873-4
Bispecific BCMA/CD24 CAR-T cells control multiple myeloma growth
Abstract
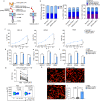
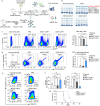
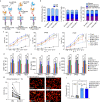
Anti-multiple myeloma B cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-specific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies represent a promising treatment strategy with high response rates in myeloma. However, durable cures following anti-BCMA CAR-T cell treatment of myeloma are rare. One potential reason is that a small subset of minimal residual myeloma cells seeds relapse. Residual myeloma cells following BCMA-CAR-T-mediated treatment show less-differentiated features and express stem-like genes, including CD24. CD24-positive myeloma cells represent a large fraction of residual myeloma cells after BCMA-CAR-T therapy. In this work, we develop CD24-CAR-T cells and test their ability to eliminate myeloma cells. We find that CD24-CAR-T cells block the CD24-Siglec-10 pathway, thereby enhancing macrophage phagocytic clearance of myeloma cells. Additionally, CD24-CAR-T cells polarize macrophages to a M1-like phenotype. A dual-targeted BCMA-CD24-CAR-T exhibits improved efficacy compared to monospecific BCMA-CAR-T-cell therapy. This work presents an immunotherapeutic approach that targets myeloma cells and promotes tumor cell clearance by macrophages.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
F.S. and F.Z. are inventors on the patent application “Bispecific BCMA-CD24-CAR-T design”, describing the therapeutic use of BCMA-CD24-CAR-T cells for the treatment of multiple myeloma. The patent number is pending. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

