Circular RNA cVIM promotes hepatic stellate cell activation in liver fibrosis via miR-122-5p/miR-9-5p-mediated TGF-β signaling cascade
- PMID: 38243118
- PMCID: PMC10798957
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-05797-3
Circular RNA cVIM promotes hepatic stellate cell activation in liver fibrosis via miR-122-5p/miR-9-5p-mediated TGF-β signaling cascade
Abstract
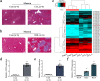
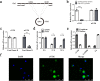
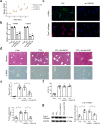
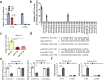
Hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation is considered as a central driver of liver fibrosis and effective suppression of HSC activation contributes to the treatment of liver fibrosis. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been reported to be important in tumor progression. However, the contributions of circRNAs in liver fibrosis remain largely unclear. The liver fibrosis-specific circRNA was explored by a circRNA microarray and cVIM (a circRNA derived from exons 4 to 8 of the vimentin gene mmu_circ_32994) was selected as the research object. Further studies revealed that cVIM, mainly expressed in the cytoplasm, may act as a sponge for miR-122-5p and miR-9-5p to enhance expression of type I TGF-β receptor (TGFBR1) and TGFBR2 and promotes activation of the TGF-β/Smad pathway, thereby accelerating the progression of liver fibrosis. Our results demonstrate a vital role for cVIM in promoting liver fibrosis progression and provide a fresh perspective on circRNAs in liver fibrosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epigenetically-Regulated MicroRNA-9-5p Suppresses the Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells via TGFBR1 and TGFBR2.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(6):2242-2252. doi: 10.1159/000484303. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29073595
-
TGF-β- and lipopolysaccharide-induced upregulation of circular RNA PWWP2A promotes hepatic fibrosis via sponging miR-203 and miR-223.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Nov 13;11(21):9569-9580. doi: 10.18632/aging.102405. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31719209 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-130b-5p promotes hepatic stellate cell activation and the development of liver fibrosis by suppressing SIRT4 expression.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Aug;25(15):7381-7394. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16766. Epub 2021 Jul 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34272822 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNA_001373 promotes liver fibrosis by regulating autophagy activation in hepatic stellate cells via the miR-142a-5p/Becn1 axis.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2024 Jan-Dec;43:9603271241265105. doi: 10.1177/09603271241265105. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39291962
-
Regulatory Functions and Mechanisms of Circular RNAs in Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Liver Fibrosis.Cells. 2023 Jan 19;12(3):378. doi: 10.3390/cells12030378. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766720 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a cross-talk between TGF-β signaling and MicroRNAs.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 25;11:1415278. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1415278. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39386739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering 3D-BMSC exosome-based hydrogels that collaboratively regulate bone microenvironment and promote osteogenesis for enhanced cell-free bone regeneration.Mater Today Bio. 2025 May 20;32:101881. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101881. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40510837 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNA-Mediated Epigenetic Regulation in Hepatic Stellate Cells of Liver Fibrosis.Noncoding RNA. 2024 Aug 7;10(4):44. doi: 10.3390/ncrna10040044. Noncoding RNA. 2024. PMID: 39195573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translational Regulators in Pulmonary Fibrosis: MicroRNAs, Long Non-Coding RNAs, and Transcript Modifications.Cells. 2025 Apr 3;14(7):536. doi: 10.3390/cells14070536. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40214489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum miR‑29 is increased in mice with early liver fibrosis.Exp Ther Med. 2024 May 15;28(1):285. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12573. eCollection 2024 Jul. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 38800048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forouzanfar MH, et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386:2287–2323. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00128-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

