Serum erythropoietin level is increased during stimulation for IVF but not in OHSS
- PMID: 38243286
- PMCID: PMC10799481
- DOI: 10.1186/s12958-023-01178-3
Serum erythropoietin level is increased during stimulation for IVF but not in OHSS
Abstract
Background: Erythropoietin (Epo) is a potent vascular growth factor that induces angiogenesis and antiapoptotic signalling. We investigated whether the development of numerous follicles and corpora lutea during in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycle affects circulating Epo levels and further, if Epo could be used as a novel marker for ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS).
Methods: 24 women were included in the uncomplicated IVF group and 35 women in the OHSS group. Repeated blood samples from both groups were analysed for Epo, progesterone, blood haemoglobin, and creatinine. Follicular fluid from the IVF group was analysed for Epo and progesterone. Repeated measure analysis was performed for the variables and circulating Epo levels were compared between the IVF group and early OHSS. Furthermore, related growth factors, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) were analysed from subgroup of women to test for correlation with Epo.
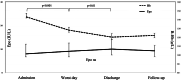
Results: During IVF, circulating Epo increased from natural mid-luteal phase to stimulated mid-luteal phase (median 9.5; 95% CI 7.2-13.4 IU/L and 12.5; 10.3-13.4 IU/L; p = 0.003). In cycles resulting in pregnancy, Epo level decreased 14 days after oocyte pick-up (OPU) and remained low thereafter. In cycles not resulting in pregnancy, Epo level increased again 35 days after OPU. Follicle fluid Epo concentration was 1.5 times higher than the serum concentration (median 15.4; 95% CI 10.4-19.2 IU/L vs. 10.2; 8.8-12.7; p = 0.006). There was no difference in circulating Epo concentration between early OHSS and uncomplicated IVF. Circulating Epo did not correlate with VEGF or HIF-1.
Conclusions: Circulating Epo levels fluctuate during IVF cycle. We hypothesise this may suggest Epo's involvement in ovarian physiology and angiogenesis. However, Epo was not a clinical marker for OHSS.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Early pregnancy; Erythropoietin; In vitro fertilization; Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
HS-P has been a member of the advisory board of Ferring Pharmaceuticals and a consultant to Merck and Orion.
Figures

References
-
- Caccamo C, Nostro L, Giorgianni G, Mondello S, Crasci E, Frisina N, et al. Behavior of vascular endothelial growth factor and erythropoietin throughout the menstrual cycle in healthy women. J Reprod Med. 2007;52(11):1035–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

