Potential role of RhoA GTPase regulation in type interferon signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 38243295
- PMCID: PMC10799493
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-024-03263-3
Potential role of RhoA GTPase regulation in type interferon signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Objective: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by abnormal activation of the type I interferon (IFN) pathway, which results in tissue inflammation and organ damage. We explored the role of the RhoA GTPase in the type I IFN activation pathway to provide a potential basis for targeting GTPase signaling for the treatment of SLE.
Methods: Total RNA was extracted from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of SLE patients and healthy controls, and the mRNA expression levels of RhoA and IFN-stimulated genes were measured by SYBR Green quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. IFN-a-stimulated response element (ISRE)-luciferase reporter gene assays and Western blotting were conducted to assess the biologic function of RhoA. An enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) measured C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10) protein expression.
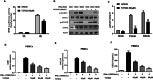
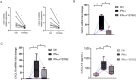
Results: Our studies demonstrate that the expression of RhoA in the PBMCs of SLE subjects was significantly higher than in healthy controls and positively correlated with type I IFN scores and type I IFN-stimulated gene (ISGs) expression levels. SiRNA-mediated knockdown of RhoA and the RhoA/ROCK inhibitor Y27632 reduced the activity of the type I IFN-induced ISRE, the signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT-1) phosphorylation, and the expression of CXCL10 and 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 1 (OAS1). Finally, we verified that Y27632 could significantly down-regulate the OAS1 and CXCL10 expression levels in the PBMCs of SLE patients.
Conclusion: Our study shows that RhoA positively regulates the activation of the type I IFN response pathway. Reducing the expression level of RhoA inhibits the abnormal activation of the type I IFN system, and the RhoA/ROCK inhibitor Y27632 decreases aberrant type I IFN signaling in SLE PBMCs, suggesting the possibility of targeting the RhoA GTPase for the treatment of SLE.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; RhoA; RhoA/ROCK inhibitor; Systemic lupus erythematosus; Type I IFN.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Update of
-
The RhoA GTPase regulates Type I Interferon Signaling in Systemic lupus erythematosus.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 20:rs.3.rs-3320841. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3320841/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Jan 20;26(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03263-3. PMID: 37790522 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Rönnblom L. The importance of the type I interferon system in autoimmunity. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016;34:21–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

