Phase 1 first-in-human dose-escalation study of ANV419 in patients with relapsed/refractory advanced solid tumors
- PMID: 38243906
- PMCID: PMC10668247
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007784
Phase 1 first-in-human dose-escalation study of ANV419 in patients with relapsed/refractory advanced solid tumors
Abstract
Background: ANV419 is a stable antibody-cytokine fusion protein consisting of interleukin-2 (IL-2) fused to an anti-IL-2 monoclonal antibody that sterically hinders binding of IL-2 to the α subunit of its receptor but has selective affinity for the receptor βγ subunits. Thus, ANV419 preferentially stimulates CD8+ effector T cells and natural killer cells which are associated with tumor killing, while minimizing the activation of immunosuppressive regulatory T cells.
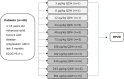
Methods: ANV419-001 is an open-label, multicenter, phase 1 study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) of ANV419. Secondary objectives were to characterize the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and tumor response. Adult patients with advanced solid tumors and disease progression after ≥1 previous line of systemic therapy were enrolled. ANV419 was administered by intravenous infusion once every 2 weeks, with a planned treatment duration of 12 months. The dose escalation part of the study explored doses 3, 6 and 12 µg/kg as single patient cohorts followed by 24-364 µg/kg in a 3+3 design. Interim results are reported here (data cut-off: March 22, 2023).
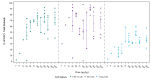
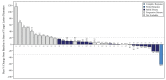
Results: Forty patients were enrolled and received at least one dose of ANV419. The MTD and RP2D were determined to be 243 µg/kg. The most common ANV419-related treatment-emergent adverse events were Grade 1 and 2 fever (31 (77.5%)), chills (23 (57.5%), vomiting (14 (35.0%)), cytokine release syndrome and nausea (12 (30.0%) each). Transient and self-limiting lymphopenia due to lymphocyte redistribution was observed in all patients. In the RP2D cohort, Grade ≥3 thrombocytopenia and fever were reported by one patient (12.5%) each. All events were manageable with standard supportive care. At doses of 243 µg/kg (RP2D/MTD), the estimated T1/2 was approximately 12 hours. At ANV419 doses ≥108 µg/kg, 64% of patients had a best response of at least SD (15 SD and 1 confirmed PR).
Conclusions: ANV419 at doses up to 243 µg/kg (the RP2D) was well tolerated and showed signs of antitumor activity in a heavily pretreated patient population with advanced solid tumors.
Trial registration number: NCT04855929.
Keywords: Immunotherapy; Natural Killer T-Cells; T-Lymphocytes.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MJ received support for attending meetings and/or travel from Roche and Takeda; participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for Novartis, Innomedica, Debiopharm, AstraZeneca and BMS. EC is employed by START and HM Hospitales Group and holds a leadership role at START, Pharma Mar, EORTC, Sanofi, BeiGene, Novartis and Merus NV; is a stockholder of START and Oncoart Associate, received grants from START, received consulting fees or honoraria from Nanobiotix, Janssen-Cilag, Roche/Genentech, TargImmune Therapeutics, Servier, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Amunix, Adcendo, Anaveon, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Chugai Pharma, MonTa, MSD Oncology, Nouscom, Novartis, OncoDNA, T-Knife, Elevation Oncology, PharmaMar, Ellipses Pharma, Syneos Health, Genmab, Diaccurate and HM Hospitales Group. HL received consulting fees from BMS, Palleon, MSD; support for attending meetings and/or travel from Amgen. JL received consulting fees for participation in an Advisory Board for Roche Genentech, GSK, Basilea and Pierre-Faber. ECdlF, GA, VSP and DH have no disclosures. DK received consulting fees from AstraZeneca; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Amgen and Sanofi; support for attending meetings and/or travel from Amgen, Roche and Sanofi; participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board from AstraZeneca, Merck, MSD. CB and SJ were employees and held stock options of Anaveon AG during the conduct of this study. EG received grants/contracts from Novartis, Roche, Thermo Fisher, AstraZeneca, Taiho, BeiGene, Janssen; consulting fees from Roche, Ellipses Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen Global Services, Seattle Genetics, Thermo Fisher, MabDiscovery, Anaveon, F-Star Therapeutics, Hengrui, Sanofi, Incyte; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or education events from Merck Sharp & Dohme, Roche, Thermo Fisher, Lilly, Novartis, SeaGen; Principal Investigator or Insitutional Co-for studies sponsored by: Adaptimmune LLC, Affimed Gmbh, Amgen SA, Anaveon AG, AstraZeneca AB, Bicycletx Ltd, BioInvent International AB, Biontech SE, Biontech Small Molecules Gmbh, Boehringer Ingelhem International Gmbh, Catalym Gmbh, Cyclacel Biopharmaceuticals, Cytovation AS, Cytomx, F.Hoffmann La Roche Ltd, F-Star Beta Limited, Genentech Inc, Genmab B.V., Hifibio Therapeutics, Hutchison Medipharma Limited, Icon, Imcheck Therapeutics, Immunocore Ltd, Incyte Corporation, Incyte Europe Sàrl, Janssen-Cilag International NV, Janssen-Cilag SA, Laboratorios Servier SL, Medimmune Llc, Merck & Co, Inc, Merck Kgga, Novartis Farmacéutica, S.A, Peptomyc, Pfizer Slu, Relay Therapeutics, Replimmune, Ribon Therapeutics, Ryvu Therapeutics SA, Seattle Genetics Inc, Sotio as, Sqz Biotechnologies, Symphogen A/S, Taiho Pharma Usa Inc and T-Knife Gmbh.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase 1 first-in-human dose-escalation study of ANV419 in patients with relapsed/refractory advanced solid tumors.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 May 3;12(5):e008847. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-008847. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38702147 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Discovery and development of ANV419, an IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody fusion protein with potent CD8+ T and natural killer cell-stimulating capacity for cancer immunotherapy.MAbs. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2381891. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2024.2381891. Epub 2024 Jul 23. MAbs. 2024. PMID: 39041287 Free PMC article.
-
Evorpacept alone and in combination with pembrolizumab or trastuzumab in patients with advanced solid tumours (ASPEN-01): a first-in-human, open-label, multicentre, phase 1 dose-escalation and dose-expansion study.Lancet Oncol. 2021 Dec;22(12):1740-1751. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00584-2. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Lancet Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34793719 Clinical Trial.
-
Nemvaleukin alfa, a modified interleukin-2 cytokine, as monotherapy and with pembrolizumab in patients with advanced solid tumors (ARTISTRY-1).J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Nov 20;12(11):e010143. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010143. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39567211 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase I/II Study of FN-1501 in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 29;15(9):2553. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092553. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37174019 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
ANV600 is a novel PD-1 targeted IL-2Rβγ agonist that selectively expands tumor antigen-specific T cells and potentiates PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor therapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Jul 15;13(7):e011905. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2025-011905. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40664449 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial treatment with upadacitinib abrogates systemic toxicity of a tumor-targeted IL-2 fusion protein.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 May 11;13(5):e010831. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010831. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40350206 Free PMC article.
-
Phase 1 first-in-human dose-escalation study of ANV419 in patients with relapsed/refractory advanced solid tumors.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 May 3;12(5):e008847. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-008847. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38702147 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Selective activation of interleukin-2/interleukin-15 receptor signaling in tumor microenvironment using paired bispecific antibodies.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Mar 25;13(3):e010650. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010650. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40132909 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and development of ANV419, an IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody fusion protein with potent CD8+ T and natural killer cell-stimulating capacity for cancer immunotherapy.MAbs. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2381891. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2024.2381891. Epub 2024 Jul 23. MAbs. 2024. PMID: 39041287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Konrad MW, Hemstreet G, Hersh EM, et al. . Pharmacokinetics of recombinant interleukin 2 in humans. Cancer Res 1990;50:2009–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
