Pulsed electric field, cryoballoon, and radiofrequency for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation ablation: a propensity score-matched comparison
- PMID: 38245007
- PMCID: PMC10823352
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/euae016
Pulsed electric field, cryoballoon, and radiofrequency for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation ablation: a propensity score-matched comparison
Abstract
Aims: Pulsed field ablation (PFA) has emerged as a novel, non-thermal energy source to selectively ablate cardiac tissue. We describe a multicentre experience on pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) via the pentaspline Farapulse™ PFA system vs. thermal-based technologies in a propensity score-matched population of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (PAF) patients.
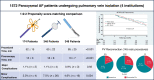
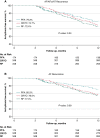
Methods and results: Propensity score matching was adopted to compare PVI-only ablation outcomes via the Farawave™ system (Group PFA), cryoballoon (Group CRYO), or focal radiofrequency (Group RF) (PFA:CRYO:RF ratio = 1:2:2). Among 1572 (mean age: 62.4 ± 11.3 years; 42.5% females) PAF patients undergoing first time PVI with either PFA (n = 174), CRYO (n = 655), or RF (n = 743), propensity score matching yielded 174 PFA, 348 CRYO, and 348 RF patients. First-pass isolation was achieved in 98.8% of pulmonary veins (PVs) with PFA, 81.5% with CRYO, and 73.1% with RF (P < 0.001). Procedural and dwell times were significantly shorter with PFA, whereas the availability of a 3D mapping system led to a significant reduction in X-ray exposure with RF. Overall complication rates were 3.4% (n = 6) with PFA, 8.6% (n = 30) with CRYO, and 5.5% (n = 19) with RF (P = 0.052). The 1-year Kaplan-Meier estimated freedom from any atrial tachyarrhythmia was 79.3% with PFA, 74.7% with CRYO, and 72.4% with RF (log-rank P-value: 0.24). Among 145 repeat ablation procedures, PV reconnection rate was 19.1% after PFA, 27.5% after CRYO, and 34.8% after RF (P = 0.01).
Conclusion: Pulsed field ablation contributed to significantly shorter procedural times. Follow-up data showed a similar arrhythmia freedom, although a higher rate of PV reconnection was documented in post-CRYO and post-RF redo procedures.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Atrial flutter; Cryoablation; Focal ablation; Pulsed field ablation; Radiofrequency; Single-shot.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests. A.N. received speaker honoraria from Boston Scientific, Biosense Webster, Abbott, Biotronik, and Medtronic; and is a consultant for Biosense Webster, Abbott, and Janssen. G.-B.C. received compensation for teaching purposes and proctoring from Medtronic, Abbott, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Acutus Medical. C.d.A. receives research grants on behalf of the centre from Biotronik, Medtronic, Abbott, LivaNova, Boston Scientific, AtriCure, Philips, and Acutus. The other authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Kuck K-H, Brugada J, Fürnkranz A, Metzner A, Ouyang F, Chun KRJet al. . Cryoballoon or radiofrequency ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2016;374:2235–45. - PubMed
-
- Aryana A, Singh SM, Mugnai G, de Asmundis C, Kowalski M, Pujara DKet al. . Pulmonary vein reconnection following catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation using the second-generation cryoballoon versus open-irrigated radiofrequency: results of a multicenter analysis. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 2016;47:341–8. - PubMed
-
- Kuck K-H, Albenque J-P, Chun KRJ, Fürnkranz A, Busch M, Elvan Aet al. . Repeat ablation for atrial fibrillation recurrence post cryoballoon or radiofrequency ablation in the FIRE AND ICE trial. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2019;12:e007247. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

