Distinguishing examples while building concepts in hippocampal and artificial networks
- PMID: 38245502
- PMCID: PMC10799871
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-44877-0
Distinguishing examples while building concepts in hippocampal and artificial networks
Abstract
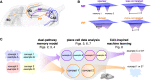
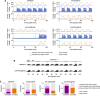
The hippocampal subfield CA3 is thought to function as an auto-associative network that stores experiences as memories. Information from these experiences arrives directly from the entorhinal cortex as well as indirectly through the dentate gyrus, which performs sparsification and decorrelation. The computational purpose for these dual input pathways has not been firmly established. We model CA3 as a Hopfield-like network that stores both dense, correlated encodings and sparse, decorrelated encodings. As more memories are stored, the former merge along shared features while the latter remain distinct. We verify our model's prediction in rat CA3 place cells, which exhibit more distinct tuning during theta phases with sparser activity. Finally, we find that neural networks trained in multitask learning benefit from a loss term that promotes both correlated and decorrelated representations. Thus, the complementary encodings we have found in CA3 can provide broad computational advantages for solving complex tasks.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A computational study on how theta modulated inhibition can account for the long temporal windows in the entorhinal-hippocampal loop.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015 Apr;120:69-83. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2015.02.002. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015. PMID: 25721691
-
Hopfield-like network with complementary encodings of memories.Phys Rev E. 2023 Nov;108(5-1):054410. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.108.054410. Phys Rev E. 2023. PMID: 38115467
-
Entorhinal cortex grid cells can map to hippocampal place cells by competitive learning.Network. 2006 Dec;17(4):447-65. doi: 10.1080/09548980601064846. Network. 2006. PMID: 17162463
-
Hippocampal place cells: parallel input streams, subregional processing, and implications for episodic memory.Hippocampus. 2006;16(9):755-64. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20203. Hippocampus. 2006. PMID: 16883558 Review.
-
A computational theory of hippocampal function, and tests of the theory: new developments.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015 Jan;48:92-147. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.11.009. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015. PMID: 25446947 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantifying information stored in synaptic connections rather than in firing patterns of neural networks.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 26:arXiv:2411.17692v1. ArXiv. 2024. PMID: 39650602 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A Comprehensive Drift-Adaptive Framework for Sustaining Model Performance in COVID-19 Detection From Dynamic Cough Audio Data: Model Development and Validation.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jun 3;27:e66919. doi: 10.2196/66919. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40459919 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McNaughton B, Morris R. Hippocampal synaptic enhancement and information storage within a distributed memory system. Trends Neurosci. 1987;10:408–415. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(87)90011-7. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

