Development and validation of cost-effective SYBR Green-based RT-qPCR and its evaluation in a sample pooling strategy for detecting SARS-CoV-2 infection in the Indonesian setting
- PMID: 38245603
- PMCID: PMC10799953
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-52250-w
Development and validation of cost-effective SYBR Green-based RT-qPCR and its evaluation in a sample pooling strategy for detecting SARS-CoV-2 infection in the Indonesian setting
Abstract
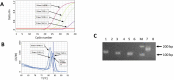
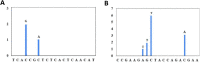
A low-cost SYBR Green-based RT-qPCR method to detect SARS-CoV-2 were developed and validated. Primers targeting a conserved and vital region of the N genes of SARS-CoV-2 were designed. In-silico study was performed to analyse the compatibility of the selected primer pair with Indonesian SARS-CoV-2 genome sequences available from the GISAID database. We determined the linearity of our new assay using serial dilution of SARS-CoV-2 RNA from clinical samples with known virus concentration. The assay was then evaluated using clinically relevant samples in comparison to a commercial TaqMan-based test kit. Finally, we applied the assay in sample pooling strategies for SARS-CoV-2 detection. The SYBR Green-based RT-qPCR method was successfully developed with sufficient sensitivity. There is a very low prevalence of genome variation in the selected N primer binding regions, indicating their high conservation. The validation of the assay using clinical samples demonstrated similar performance to the TaqMan method suggesting the SYBR methods is reliable. The pooling strategy by combining 5 RNA samples for SARS-CoV-2 detection using the SYBR RT-qPCR methods is feasible and provides a high diagnostic yield. However, when dealing with samples having a very low viral load, it may increase the risk of missing positive cases.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

