High-intensity intermittent training ameliorates methotrexate-induced acute lung injury
- PMID: 38245672
- PMCID: PMC10800073
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-024-02853-w
High-intensity intermittent training ameliorates methotrexate-induced acute lung injury
Abstract
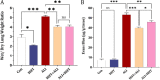
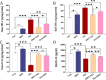
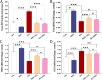
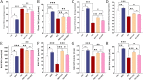
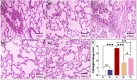
Inflammation and oxidative stress are recognized as two primary causes of lung damage induced by methotrexate, a drug used in the treatment of cancer and immunological diseases. This drug triggers the generation of oxidants, leading to lung injury. Given the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of high-intensity intermittent training (HIIT), our aim was to evaluate the therapeutic potential of HIIT in mitigating methotrexate-induced lung damage in rats. Seventy male Wistar rats were randomly divided into five groups: CTL (Control), HIIT (High-intensity intermittent training), ALI (Acute Lung Injury), HIIT+ALI (pretreated with HIIT), and ALI + HIIT (treated with HIIT).HIIT sessions were conducted for 8 weeks. At the end of the study, assessments were made on malondialdehyde, total antioxidant capacity (TAC), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (Gpx), myeloperoxidase (MPO), interleukin 10 (IL-10), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), gene expression of T-bet, GATA3, FOXP3, lung wet/dry weight ratio, pulmonary capillary permeability, apoptosis (Caspase-3), and histopathological indices.Methotrexate administration resulted in increased levels of TNF-α, MPO, GATA3, caspase-3, and pulmonary edema indices, while reducing the levels of TAC, SOD, Gpx, IL-10, T-bet, and FOXP3. Pretreatment and treatment with HIIT reduced the levels of oxidant and inflammatory factors, pulmonary edema, and other histopathological indicators. Concurrently, HIIT increased the levels of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory factors.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; High-intensity intermittent training; Inflammatory factors; Methotrexate; Mohammad Amin Rajizadeh, Mahdiyeh Haj Hosseini, Mina Bahrami, Faegheh Bahri and Fahimeh Rostamabadi equally contributed as first author.; Oxidative stress; Therapeutic effects.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Kalemci S, Dirican N, Cetin E, Sözen H, Uner A, Yaylali A, Aksun S, Karacam V, Ulger E, Sütcü R. The efficacy of minocycline against methotrexate-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17(24):3334–3340. - PubMed
-
- Hsu P-C, Lan J-L, Hsieh T-Y, Jan Y-J. Huang W-N: methotrexate pneumonitis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. J Microbiol Immunol Infect Wei Mian yu gan ran za zhi. 2003;36(2):137–140. - PubMed
-
- Fan J, Ye RD, Malik AB. Transcriptional mechanisms of acute lung injury. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys. 2001;281(5):L1037–L1050. - PubMed
-
- Zhu J, Jankovic D, Oler AJ, Wei G, Sharma S, Hu G, Guo L, Yagi R, Yamane H, Punkosdy G. The transcription factor T-bet is induced by multiple pathways and prevents an endogenous Th2 cell program during Th1 cell responses. Immunity. 2012;37(4):660–673. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.09.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

