Lead generation of UPPS inhibitors targeting MRSA: Using 3D-QSAR pharmacophore modeling, virtual screening, molecular docking, and molecular dynamic simulations
- PMID: 38245752
- PMCID: PMC10800075
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-023-01110-1
Lead generation of UPPS inhibitors targeting MRSA: Using 3D-QSAR pharmacophore modeling, virtual screening, molecular docking, and molecular dynamic simulations
Abstract
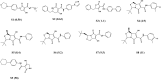
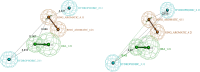
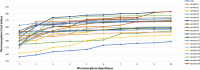
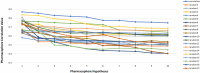
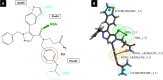
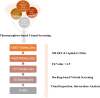
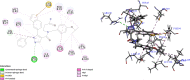
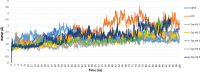
Undecaprenyl Pyrophosphate Synthase (UPPS) is a vital target enzyme in the early stages of bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. UPPS inhibitors have antibacterial activity against resistant strains such as MRSA and VRE. In this study, we used several consecutive computer-based protocols to identify novel UPPS inhibitors. The 3D QSAR pharmacophore model generation (HypoGen algorithm) protocol was used to generate a valid predictive pharmacophore model using a set of UPPS inhibitors with known reported activity. The developed model consists of four pharmacophoric features: one hydrogen bond acceptor, two hydrophobic, and one aromatic ring. It had a correlation coefficient of 0.86 and a null cost difference of 191.39, reflecting its high predictive power. Hypo1 was proven to be statistically significant using Fischer's randomization at a 95% confidence level. The validated pharmacophore model was used for the virtual screening of several databases. The resulting hits were filtered using SMART and Lipinski filters. The hits were docked into the binding site of the UPPS protein, affording 70 hits with higher docking affinities than the reference compound (6TC, - 21.17 kcal/mol). The top five hits were selected through extensive docking analysis and visual inspection based on docking affinities, fit values, and key residue interactions with the UPPS receptor. Moreover, molecular dynamic simulations of the top hits were performed to confirm the stability of the protein-ligand complexes, yielding five promising novel UPPS inhibitors.
Keywords: 3D QSAR pharmacophore; Antibacterial; Bacterial resistance; Drug repurposing; Dynamic simulations; HypoGen algorithm; Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; Molecular docking; UPPS.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sit PS, Teh CS, Idris N, Sam IC, Syed Omar SF, Sulaiman H, et al. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection and the molecular characteristics of MRSA bacteraemia over a two-year period in a tertiary teaching hospital in Malaysia. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2384-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
