Alzheimer's Disease Biomarker Analysis Using Targeted Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 38246483
- PMCID: PMC10926085
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2024.100721
Alzheimer's Disease Biomarker Analysis Using Targeted Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
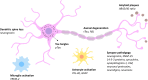
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by several neuropathological changes, mainly extracellular amyloid aggregates (plaques), intraneuronal inclusions of phosphorylated tau (tangles), as well as neuronal and synaptic degeneration, accompanied by tissue reactions to these processes (astrocytosis and microglial activation) that precede neuronal network disturbances in the symptomatic phase of the disease. A number of biomarkers for these brain tissue changes have been developed, mainly using immunoassays. In this review, we discuss how targeted mass spectrometry (TMS) can be used to validate and further characterize classes of biomarkers reflecting different AD pathologies, such as tau- and amyloid-beta pathologies, synaptic dysfunction, lysosomal dysregulation, and axonal damage, and the prospect of using TMS to measure these proteins in clinical research and diagnosis. TMS advantages and disadvantages in relation to immunoassays are discussed, and complementary aspects of the technologies are discussed.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; amyloid; biomarkers; targeted mass spectrometry; tau.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest K. B. has served as a consultant and at advisory boards for Acumen, ALZPath, BioArctic, Biogen, Eisai, Julius Clinical, Lilly, Novartis, Ono Pharma, Prothena, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens Healthineers; has served at data monitoring committees for Julius Clinical and Novartis; has given lectures, produced educational materials, and participated in educational programs for Biogen, Eisai, and Roche Diagnostics; and is a cofounder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program, outside the work presented in this article. H.Z. has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for AbbVie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, CogRx, De nali, Eisai, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave, has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Alzecure, Biogen, and Roche, and is a cofounder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work).
Figures

References
-
- Alzheimer A., Stelzmann R.A., Schnitzlein H.N., Murtagh F.R. An English translation of Alzheimer's 1907 paper, “Uber eine eigenartige Erkankung der Hirnrinde”. Clin. Anat. 1995;8:429–431. - PubMed
-
- Hardy J.A., Higgins G.A. Alzheimer's disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science. 1992;256:184–185. - PubMed
-
- McDade E., Cummings J.L., Dhadda S., Swanson C.J., Reyderman L., Kanekiyo M., et al. Lecanemab in patients with early Alzheimer's disease: detailed results on biomarker, cognitive, and clinical effects from the randomized and open-label extension of the phase 2 proof-of-concept study. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2022;14:191. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mintun M.A., Lo A.C., Duggan Evans C., Wessels A.M., Ardayfio P.A., Andersen S.W., et al. Donanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021;384:1691–1704. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

