Protozoan-Derived Cytokine-Transgenic Macrophages Reverse Hepatic Fibrosis
- PMID: 38247166
- PMCID: PMC10987136
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202308750
Protozoan-Derived Cytokine-Transgenic Macrophages Reverse Hepatic Fibrosis
Abstract
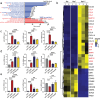
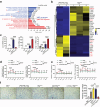
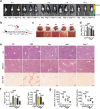
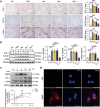
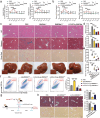
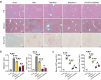
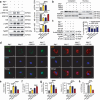
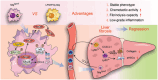
Macrophage therapy for liver fibrosis is on the cusp of meaningful clinical utility. Due to the heterogeneities of macrophages, it is urgent to develop safer macrophages with a more stable and defined phenotype for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Herein, a new macrophage-based immunotherapy using macrophages stably expressing a pivotal cytokine from Toxoplasma gondii, a parasite that infects ≈ 2 billion people is developed. It is found that Toxoplasma gondii macrophage migration inhibitory factor-transgenic macrophage (Mφtgmif) shows stable fibrinolysis and strong chemotactic capacity. Mφtgmif effectively ameliorates liver fibrosis and deactivates aHSCs by recruiting Ly6Chi macrophages via paracrine CCL2 and polarizing them into the restorative Ly6Clo macrophage through the secretion of CX3CL1. Remarkably, Mφtgmif exhibits even higher chemotactic potential, lower grade of inflammation, and better therapeutic effects than LPS/IFN-γ-treated macrophages, making macrophage-based immune therapy more efficient and safer. Mechanistically, TgMIF promotes CCL2 expression by activating the ERK/HMGB1/NF-κB pathway, and this event is associated with recruiting endogenous macrophages into the fibrosis liver. The findings do not merely identify viable immunotherapy for liver fibrosis but also suggest a therapeutic strategy based on the evolutionarily designed immunomodulator to treat human diseases by modifying the immune microenvironment.
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii; Toxoplasma gondii macrophage migration inhibitory factors; immunotherapy; liver fibrosis; macrophages; polarization.
© 2024 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
