Rice Byproduct Compounds: From Green Extraction to Antioxidant Properties
- PMID: 38247461
- PMCID: PMC10812773
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13010035
Rice Byproduct Compounds: From Green Extraction to Antioxidant Properties
Abstract
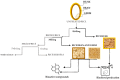
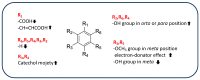
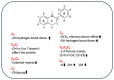
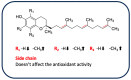
Currently, rice (Oryza sativa L.) production and consumption is increasing worldwide, and many efforts to decrease the substantial impact of its byproducts are needed. In recent years, the interest in utilizing rice kernels, husk, bran, and germ for the recovery of different molecules, from catalysts (to produce biodiesel) to bioactive compounds, has grown. In fact, rice byproducts are rich in secondary metabolites (phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and tocopherols) with different types of bioactivity, mainly antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, and anti-inflammatory, which make them useful as functional ingredients. In this review, we focus our attention on the recovery of antioxidant compounds from rice byproducts by using innovative green techniques that can overcome the limitations of traditional extraction processes, such as their environmental and economic impact. In addition, traditional assays and more innovative methodologies to evaluate the antioxidant activity are discussed. Finally, the possible molecular mechanisms of action of the rice byproduct antioxidant compounds (phenolic acids, flavonoids, γ-oryzanol, and vitamin E) are discussed as well. In the future, it is expected that rice byproduct antioxidants will be important food ingredients that reduce the risk of the development of several human disorders involving oxidative stress, such as metabolic diseases, inflammatory disorders, and cancer.
Keywords: antioxidant compounds; bioactives; flavonoids; functional ingredients; green methodologies; innovative extraction techniques; phenolic acids; rice byproducts; structure-activity relationship; vitamin E.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rice Bran: From Waste to Nutritious Food Ingredients.Nutrients. 2023 May 28;15(11):2503. doi: 10.3390/nu15112503. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37299466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rice Nutraceuticals and Bioactive Compounds: Extraction, Characterization and Antioxidant Activity: A Review.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023;26(15):2625-2643. doi: 10.2174/1386207326666230512144834. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023. PMID: 37183472
-
Enhancement Methods of Antioxidant Capacity in Rice Bran: A Review.Foods. 2022 Sep 26;11(19):2994. doi: 10.3390/foods11192994. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36230070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rice antioxidants: phenolic acids, flavonoids, anthocyanins, proanthocyanidins, tocopherols, tocotrienols, γ-oryzanol, and phytic acid.Food Sci Nutr. 2014 Mar;2(2):75-104. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.86. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Food Sci Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24804068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of different treatments on the antioxidant properties and phenolic compounds of rice bran and rice husk.Food Chem. 2014 Aug 15;157:457-63. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.02.061. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24679804
Cited by
-
Advancements in rice disease detection through convolutional neural networks: A comprehensive review.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 19;10(12):e33328. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33328. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39021980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Human Milk Oligosaccharides and Probiotics on Gut Microbiome and Mood in Autism: A Case Report.Microorganisms. 2024 Aug 9;12(8):1625. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081625. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203467 Free PMC article.
-
Synbiotic yogurt with nanoparticle entrapped rice straw hemicellulose for immediate probiotic support and prebiotic delivery.NPJ Sci Food. 2025 Aug 18;9(1):177. doi: 10.1038/s41538-025-00539-z. NPJ Sci Food. 2025. PMID: 40825779 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Heavy Metal Pollution on Soil Nitrogen Transformation and Rice Volatile Organic Compounds under Different Water Management Practices.Plants (Basel). 2024 Mar 18;13(6):871. doi: 10.3390/plants13060871. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38592896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preservation of freshly-cut lemon slices using alginate-based coating functionalized with antioxidant enzymatically hydrolyzed rice straw-hemicellulose.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 8;14(1):27176. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77670-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39511274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Papargyropoulou E., Lozano R., Steinberger J.K., Wright N., Ujang Z. The food waste hierarchy as a framework for the management of food surplus and food waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2014;76:106–115. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.04.020. - DOI
-
- United Nations. [(accessed on 7 November 2023)]. Available online: https://documents-dds-ny.un.org/doc/UNDOC/GEN/N15/291/89/PDF/N1529189.pd....
-
- FAOSTAT Food and Agriculture Data. [(accessed on 7 November 2023)]. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC.
-
- Sena S., Chakraborty R., Kalit P. Rice—Not just a staple food: A comprehensive review on its phytochemicals. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020;97:265–285. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.01.022. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

