Albumin Redox Modifications Promote Cell Calcification Reflecting the Impact of Oxidative Status on Aortic Valve Disease and Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 38247532
- PMCID: PMC10812654
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13010108
Albumin Redox Modifications Promote Cell Calcification Reflecting the Impact of Oxidative Status on Aortic Valve Disease and Atherosclerosis
Abstract
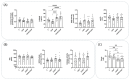
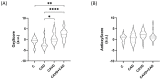
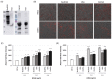
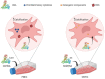
Calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD) and coronary artery disease (CAD) are related cardiovascular diseases in which common mechanisms lead to tissue calcification. Oxidative stress plays a key role in these diseases and there is also evidence that the redox state of serum albumin exerts a significant influence on these conditions. To further explore this issue, we used multimarker scores (OxyScore and AntioxyScore) to assess the global oxidative status in patients with CAVD, with and without CAD, also evaluating their plasma thiol levels. In addition, valvular interstitial cells were treated with reduced, oxidized, and native albumin to study how this protein and its modifications affect cell calcification. The differences we found suggest that oxidative status is distinct in CAVD and CAD, with differences in redox markers and thiol levels. Importantly, the in vitro interstitial cell model revealed that modified albumin affects cell calcification, accelerating this process. Hence, we show here the importance of the redox system in the development of CAVD, emphasizing the relevance of multimarker scores, while also offering evidence of how the redox state of albumin influences vascular calcification. These data highlight the relevance of understanding the overall redox processes involved in these diseases, opening the door to new studies on antioxidants as potential therapies for these patients.
Keywords: aortic stenosis; aortic valve; artery; calcification; interstitial cells; multimarker score; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Influence of Coronary Artery Disease in the Development of Aortic Stenosis and the Importance of the Albumin Redox State.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Feb 5;11(2):317. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020317. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204200 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress in a Cell Spheroid Model of Calcific Aortic Valve Disease.Cells. 2023 Dec 25;13(1):45. doi: 10.3390/cells13010045. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38201249 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-β1 promotes fibrosis but attenuates calcification of valvular tissue applied as a three-dimensional calcific aortic valve disease model.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020 Nov 1;319(5):H1123-H1141. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00651.2019. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32986963
-
Oxidative stress and valvular endothelial cells in aortic valve calcification.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jul;163:114775. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114775. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37116353 Review.
-
Contribution of Oxidative Stress (OS) in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease (CAVD): From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Targets.Cells. 2022 Aug 27;11(17):2663. doi: 10.3390/cells11172663. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36078071 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The association between the albumin to globulin ratio and thoracic spine bone mineral density in adolescents: NHANES 2011-2016.Front Nutr. 2025 Jun 26;12:1560013. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1560013. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40661684 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Diabetes Mellitus and Kidney Dysfunction on Oxidative Stress, a Reflection of the Multisystem Interactions in Aortic Stenosis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jul 18;14(7):888. doi: 10.3390/antiox14070888. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722992 Free PMC article.
-
Stable Nitroxide as Diagnostic Tools for Monitoring of Oxidative Stress and Hypoalbuminemia in the Context of COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 24;25(15):8045. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158045. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Katz R., Wong N.D., Kronmal R., Takasu J., Shavelle D.M., Probstfield J.L., Bertoni A.G., Budoff M.J., O’Brien K.D. Features of the metabolic syndrome and diabetes mellitus as predictors of aortic valve calcification in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2006;113:2113–2119. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.598086. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van der Wal A.C., Becker A.E., van der Loos C.M., Das P.K. Site of intimal rupture or erosion of thrombosed coronary atherosclerotic plaques is characterized by an inflammatory process irrespective of the dominant plaque morphology. Circulation. 1994;89:36–44. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.89.1.36. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- PI18/00995, PI20/00763, PI21/00384, PI23/00182, AC22/00022, CPII20/00022, FI19/00157/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- 2020, SEC/FEC-INV-BAS23/Sociedad Española de Cardiología
- P2022/BMD-7223 CIFRA_COR-CM/European Union, Biomedicine Network Comunidad de Madrid
- RED2022-134511-T/Spanish Network
- SBPLY/19/180501/000226, SBPLY/21/180501/000078/Regional Government of Castile-La Mancha
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

