Extracellular Vesicles from a Biofilm of a Clinical Isolate of Candida albicans Negatively Impact on Klebsiella pneumoniae Adherence and Biofilm Formation
- PMID: 38247639
- PMCID: PMC10812662
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13010080
Extracellular Vesicles from a Biofilm of a Clinical Isolate of Candida albicans Negatively Impact on Klebsiella pneumoniae Adherence and Biofilm Formation
Abstract
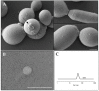
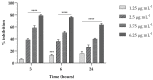
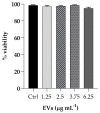
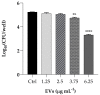
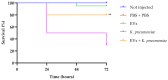
The opportunistic human fungal pathogen Candida albicans produces and releases into the surrounding medium extracellular vesicles (EVs), which are involved in some processes as communication between fungal cells and host-pathogen interactions during infection. Here, we have conducted the isolation of EVs produced by a clinical isolate of C. albicans during biofilm formation and proved their effect towards the ability of the Gram-negative bacterial pathogen Klebsiella pneumoniae to adhere to HaCaT cells and form a biofilm in vitro. The results represent the first evidence of an antagonistic action of fungal EVs against bacteria.
Keywords: Gram-negative bacteria; biofilm; candidiasis; extracellular vesicles; pathogenic fungi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

