Effects of Impulsivity and Interpersonal Problems on Adolescent Depression: A Cross-Lagged Study
- PMID: 38247704
- PMCID: PMC10813366
- DOI: 10.3390/bs14010052
Effects of Impulsivity and Interpersonal Problems on Adolescent Depression: A Cross-Lagged Study
Abstract
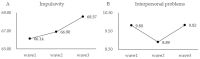
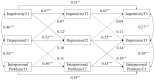
The dynamic changes over time in the relationships between impulsivity, interpersonal problems, and depression warrant further exploration. This study delves into the roles of impulsivity and interpersonal issues in the progression of adolescent depression over a year, using a sample of 271 Chinese adolescents (51.7% male, Mage = 12.60 ± 0.69). At three time points, impulsivity levels were assessed with the Chinese version of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale-11, interpersonal problems with the Adolescent Self-Rating Life Events Check List, and depression with the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale. Results revealed that both impulsivity and interpersonal problems serve as risk factors for depression, but the primary risk factor shifted over time. In early middle school stages, impulsivity was the predominant risk factor, while in later stages, interpersonal problems became the primary risk factor. These findings carry significant implications for directing prevention efforts and interventions for adolescent depression.
Keywords: adolescent; cross-lagged model; depression; impulsivity; interpersonal problems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Interpersonal Problems and Family Environment in the Association Between Impulsivity and Suicidal Ideation: A Moderate Mediation Model.J Nerv Ment Dis. 2019 Jan;207(1):22-28. doi: 10.1097/NMD.0000000000000916. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2019. PMID: 30575704
-
The Relationship between Impulsivity and Internet Gaming Disorder in Young Adults: Mediating Effects of Interpersonal Relationships and Depression.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Mar 6;15(3):458. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15030458. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29509708 Free PMC article.
-
Impulsivity, Self-control, Interpersonal Influences, and Maladaptive Cognitions as Factors of Internet Gaming Disorder Among Adolescents in China: Cross-sectional Mediation Study.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Oct 27;23(10):e26810. doi: 10.2196/26810. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34704960 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale- short form among Indian adolescents.Asian J Psychiatr. 2018 Oct;37:172-177. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Asian J Psychiatr. 2018. PMID: 30308462
-
The relationship between impulsivity and Internet addiction in a sample of Chinese adolescents.Eur Psychiatry. 2007 Oct;22(7):466-71. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2007.05.004. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Eur Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17765486
References
-
- Yang D., Wang G., Dong Q. Depression and anxiety of secondary school students: Structure and development. Psychol. Dev. Educ. 2000;16:12–17.
-
- Liu Y., Merritt D.H. Examining the association between parenting and childhood depression among Chinese children and adolescents: A systematic literature review. Child Youth Serv. Rev. 2018;88:316–332. doi: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2018.03.019. - DOI
-
- Liu F., Song X., Shang X., Wu M., Sui M., Dong Y., Liu X. A meta-analysis of detection rate of depression symptoms among middle school students. Chin. Ment. Health J. 2020;34:123–128.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources