Novel Therapeutic Hybrid Systems Using Hydrogels and Nanotechnology: A Focus on Nanoemulgels for the Treatment of Skin Diseases
- PMID: 38247768
- PMCID: PMC10815052
- DOI: 10.3390/gels10010045
Novel Therapeutic Hybrid Systems Using Hydrogels and Nanotechnology: A Focus on Nanoemulgels for the Treatment of Skin Diseases
Abstract
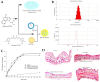
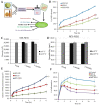
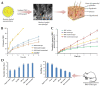
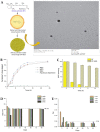
Topical and transdermal drug delivery are advantageous administration routes, especially when treating diseases and conditions with a skin etiology. Nevertheless, conventional dosage forms often lead to low therapeutic efficacy, safety issues, and patient noncompliance. To tackle these issues, novel topical and transdermal platforms involving nanotechnology have been developed. This review focuses on the latest advances regarding the development of nanoemulgels for skin application, encapsulating a wide variety of molecules, including already marketed drugs (miconazole, ketoconazole, fusidic acid, imiquimod, meloxicam), repurposed marketed drugs (atorvastatin, omeprazole, leflunomide), natural-derived compounds (eucalyptol, naringenin, thymoquinone, curcumin, chrysin, brucine, capsaicin), and other synthetic molecules (ebselen, tocotrienols, retinyl palmitate), for wound healing, skin and skin appendage infections, skin inflammatory diseases, skin cancer, neuropathy, or anti-aging purposes. Developed formulations revealed adequate droplet size, PDI, viscosity, spreadability, pH, stability, drug release, and drug permeation and/or retention capacity, having more advantageous characteristics than current marketed formulations. In vitro and/or in vivo studies established the safety and efficacy of the developed formulations, confirming their therapeutic potential, and making them promising platforms for the replacement of current therapies, or as possible adjuvant treatments, which might someday effectively reach the market to help fight highly incident skin or systemic diseases and conditions.
Keywords: anti-aging; nanoemulgels; nanoemulsions; neuropathy; skin cancer; skin infection; skin inflammation; topical administration; transdermal administration; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


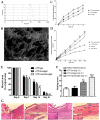
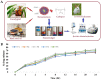
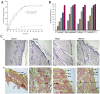
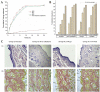
References
-
- Abdo J.M., Sopko N.A., Milner S.M. The Applied Anatomy of Human Skin: A Model for Regeneration. Wound Med. 2020;28:100179. doi: 10.1016/j.wndm.2020.100179. - DOI
-
- Xie J., Hao T., Li C., Wang X., Yu X., Liu L. Automatic Evaluation of Stratum Basale and Dermal Papillae Using Ultrahigh Resolution Optical Coherence Tomography. Biomed. Signal Process Control. 2019;53:101527. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2019.04.004. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

