Studies on Loading Salicylic Acid in Xerogel Films of Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid
- PMID: 38247777
- PMCID: PMC10815332
- DOI: 10.3390/gels10010054
Studies on Loading Salicylic Acid in Xerogel Films of Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid
Abstract
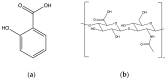
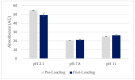
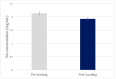
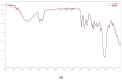
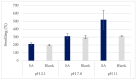
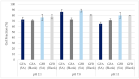
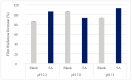
During the last decades, salicylic acid (SA) and hyaluronic acid (HA) have been studied for a wide range of cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications. The current study investigated the drug loading potential of SA in HA-based crosslinked hydrogel films using a post-loading (osmosis) method of the unmedicated xerogels from saturated aqueous solutions of salicylic acid over a range of pH values. The films were characterized with Fourier-transform infra-red spectroscopy (FT-IR) and ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometry in order to elucidate the drug loading profile and the films' integrity during the loading process. Additional studies on their weight loss (%), gel fraction (%), thickness increase (%) and swelling (%) were performed. Overall, the studies showed significant film disintegration at highly acidic and basic solutions. No drug loading occurred at neutral and basic pH, possibly due to the anionic repulsion between SA and HA, whereas at, pH 2.1, the drug loading was promising and could be detected via UV-Vis analysis of the medicated solutions, with the SA concentration in the xerogel films at 28% w/w.
Keywords: drug loading; hyaluronic acid; hydrogels; salicylic acid; xerogels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Novel salicylic acid-based chemically crosslinked pH-sensitive hydrogels as potential drug delivery systems.Int J Pharm. 2017 Aug 7;528(1-2):406-415. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.05.047. Epub 2017 May 27. Int J Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28559214
-
Effect of hyaluronic acid initial concentration on cross-linking efficiency of hyaluronic acid - based hydrogels used in biomedical and cosmetic applications.Pharmazie. 2017 Feb 1;72(2):81-86. doi: 10.1691/ph.2017.6133. Pharmazie. 2017. PMID: 29441857
-
3D Bioprinting of the Sustained Drug Release Wound Dressing with Double-Crosslinked Hyaluronic-Acid-Based Hydrogels.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Sep 27;11(10):1584. doi: 10.3390/polym11101584. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31569810 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and characterization of hyaluronic acid hydrogels crosslinked using a solvent-free process for potential biomedical applications.Carbohydr Polym. 2018 Feb 1;181:1194-1205. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.12.015. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Carbohydr Polym. 2018. PMID: 29253949 Free PMC article.
-
Highly stretchable HA/SA hydrogels for tissue engineering.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018 Apr;29(5):543-561. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2018.1426425. Epub 2018 Jan 16. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018. PMID: 29316854
References
-
- Monou P.K., Mamaligka A.M., Tzimtzimis E.K., Tzetzis D., Vergkizi-Nikolakaki S., Vizirianakis I.S., Andriotis E.G., Eleftheriadis G.K., Fatouros D.G. Fabrication and Preliminary In Vitro Evaluation of 3D-Printed Alginate Films with Cannabidiol (CBD) and Cannabigerol (CBG) Nanoparticles for Potential Wound-Healing Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14:1637. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081637. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

