COVID-19 Detection and Diagnosis Model on CT Scans Based on AI Techniques
- PMID: 38247956
- PMCID: PMC10813639
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering11010079
COVID-19 Detection and Diagnosis Model on CT Scans Based on AI Techniques
Abstract
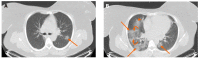
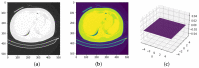
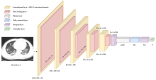
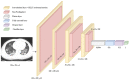
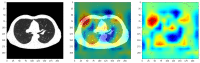
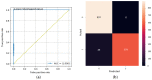
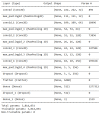
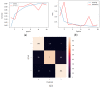
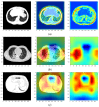
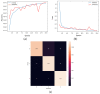
The end of 2019 could be mounted in a rudimentary framing of a new medical problem, which globally introduces into the discussion a fulminant outbreak of coronavirus, consequently spreading COVID-19 that conducted long-lived and persistent repercussions. Hence, the theme proposed to be solved arises from the field of medical imaging, where a pulmonary CT-based standardized reporting system could be addressed as a solution. The core of it focuses on certain impediments such as the overworking of doctors, aiming essentially to solve a classification problem using deep learning techniques, namely, if a patient suffers from COVID-19, viral pneumonia, or is healthy from a pulmonary point of view. The methodology's approach was a meticulous one, denoting an empirical character in which the initial stage, given using data processing, performs an extraction of the lung cavity from the CT scans, which is a less explored approach, followed by data augmentation. The next step is comprehended by developing a CNN in two scenarios, one in which there is a binary classification (COVID and non-COVID patients), and the other one is represented by a three-class classification. Moreover, viral pneumonia is addressed. To obtain an efficient version, architectural changes were gradually made, involving four databases during this process. Furthermore, given the availability of pre-trained models, the transfer learning technique was employed by incorporating the linear classifier from our own convolutional network into an existing model, with the result being much more promising. The experimentation encompassed several models including MobileNetV1, ResNet50, DenseNet201, VGG16, and VGG19. Through a more in-depth analysis, using the CAM technique, MobilneNetV1 differentiated itself via the detection accuracy of possible pulmonary anomalies. Interestingly, this model stood out as not being among the most used in the literature. As a result, the following values of evaluation metrics were reached: loss (0.0751), accuracy (0.9744), precision (0.9758), recall (0.9742), AUC (0.9902), and F1 score (0.9750), from 1161 samples allocated for each of the three individual classes.
Keywords: COVID-19; CT scans; MobileNetV1; convolutional neural network.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PulDi-COVID: Chronic obstructive pulmonary (lung) diseases with COVID-19 classification using ensemble deep convolutional neural network from chest X-ray images to minimize severity and mortality rates.Biomed Signal Process Control. 2023 Mar;81:104445. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2022.104445. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2023. PMID: 36466567 Free PMC article.
-
Automated detection of COVID-19 from CT scan using convolutional neural network.Biocybern Biomed Eng. 2021 Apr-Jun;41(2):572-588. doi: 10.1016/j.bbe.2021.04.006. Epub 2021 Apr 30. Biocybern Biomed Eng. 2021. PMID: 33967366 Free PMC article.
-
CovH2SD: A COVID-19 detection approach based on Harris Hawks Optimization and stacked deep learning.Expert Syst Appl. 2021 Dec 30;186:115805. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115805. Epub 2021 Sep 5. Expert Syst Appl. 2021. PMID: 34511738 Free PMC article.
-
Development and integration of VGG and dense transfer-learning systems supported with diverse lung images for discovery of the Coronavirus identity.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;32:101004. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.101004. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35822170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 diagnosis: A comprehensive review of pre-trained deep learning models based on feature extraction algorithm.Results Eng. 2023 Jun;18:101020. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101020. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Results Eng. 2023. PMID: 36945336 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Arboviruses and COVID-19: Global Health Challenges and Human Enhancement Technologies.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Jul 1;12(7):725. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12070725. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Oct 5, 2020. [(accessed on 22 August 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

