Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: How Machine Learning Can Help Distinguish between Infections and Flares
- PMID: 38247967
- PMCID: PMC11154352
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering11010090
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: How Machine Learning Can Help Distinguish between Infections and Flares
Abstract
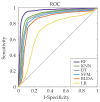
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a multifaceted autoimmune ailment that impacts multiple bodily systems and manifests with varied clinical manifestations. Early detection is considered the most effective way to save patients' lives, but detecting severe SLE activity in its early stages is proving to be a formidable challenge. Consequently, this work advocates the use of Machine Learning (ML) algorithms for the diagnosis of SLE flares in the context of infections. In the pursuit of this research, the Random Forest (RF) method has been employed due to its performance attributes. With RF, our objective is to uncover patterns within the patient data. Multiple ML techniques have been scrutinized within this investigation. The proposed system exhibited around a 7.49% enhancement in accuracy when compared to k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) algorithm. In contrast, the Support Vector Machine (SVM), Binary Linear Discriminant Analysis (BLDA), Decision Trees (DT) and Linear Regression (LR) methods demonstrated inferior performance, with respective values around 81%, 78%, 84% and 69%. It is noteworthy that the proposed method displayed a superior area under the curve (AUC) and balanced accuracy (both around 94%) in comparison to other ML approaches. These outcomes underscore the feasibility of crafting an automated diagnostic support method for SLE patients grounded in ML systems.
Keywords: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus; artificial intelligence; machine learning; medical treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Machine learning, a new tool for the detection of immunodeficiency patterns in systemic lupus erythematosus.J Investig Med. 2023 Oct;71(7):742-752. doi: 10.1177/10815589231171404. Epub 2023 May 9. J Investig Med. 2023. PMID: 37158077
-
Random forests algorithm boosts genetic risk prediction of systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 15;13:902793. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.902793. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36046232 Free PMC article.
-
Cuproptosis-related gene identification and immune infiltration analysis in systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2023 May 29;14:1157196. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1157196. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37313407 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence in clinical care amidst COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021;19:2833-2850. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.05.010. Epub 2021 May 7. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34025952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and validation of a risk calculator to differentiate flares from infections in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with fever.Autoimmun Rev. 2015 Jul;14(7):586-93. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Autoimmun Rev. 2015. PMID: 25703012 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced Data Mining and Visualization of Sensory-Graph-Modeled Datasets through Summarization.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 14;24(14):4554. doi: 10.3390/s24144554. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065952 Free PMC article.
-
Application of the Random Forest Algorithm for Accurate Bipolar Disorder Classification.Life (Basel). 2025 Mar 3;15(3):394. doi: 10.3390/life15030394. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40141739 Free PMC article.
-
Innovation through Artificial Intelligence in Triage Systems for Resource Optimization in Future Pandemics.Biomimetics (Basel). 2024 Jul 18;9(7):440. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9070440. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056881 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Factors for Mortality in Hepatocellular Carcinoma at Diagnosis: Development of a Predictive Model Using Artificial Intelligence.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 13;14(4):406. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14040406. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38396445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cortés Verdú R., Pego-Reigosa J.M., Seoane-Mato D., Morcillo Valle M., Palma Sánchez D., Moreno Martínez M.J., Mayor González M., Atxotegi Sáenz de Buruaga J., Urionagüena Onaindia I., Blanco Cáceres B.A., et al. Prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus in Spain: Higher than previously reported in other countries? Rheumatology. 2020;59:2556–2562. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bandinelli F., Bombardieri S., Matucci M., Delle Sedie A. Systemic lupus erythematosus joint involvement—What does musculoskeletal ultrasound provide Us? Eur. Musculoskelet. Rev. 2012;7:221–223.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

