Efficiency of Simulation-Based Learning Using an ABC POCUS Protocol on a High-Fidelity Simulator
- PMID: 38248050
- PMCID: PMC10814096
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14020173
Efficiency of Simulation-Based Learning Using an ABC POCUS Protocol on a High-Fidelity Simulator
Abstract
Critically ill patients with rapidly deteriorating clinical status secondary to respiratory and cardio-vascular compromise are at risk for immediate collapse if the underlying pathology is not recognized and treated. Rapid diagnosis is of utmost importance regardless of the setting. Although there are data to support the use of point-of-care ultrasound in critical patients, there is no consensus about the best educational strategy to implement. We designed a curriculum based on the ABC (Airway, Breathing, Circulation) protocol that covers essential airway, lung, and cardiac ultrasound skills needed for fast diagnosis in critical patients and applied it in high-fidelity simulation-based medical education sessions for anesthesia and intensive care residents year one and two. After theoretical and practical assessments, our results show statistical differences in the theoretical knowledge and above-average results in practical assessment. Our proposed curriculum based on a simple ABC POCUS protocol, with an Airway, Breathing, and Circulation approach, is useful in teaching ultrasound basics regarding airway, lung, and cardiac examination using high-fidelity simulation training to anesthesia and intensive care residents, but further research is needed to establish the utility of Simulation-Based Medical Education in Point of Care Ultrasound in the critical patient.
Keywords: airway ultrasound; critical patient ultrasound; heart ultrasound; lung ultrasound; point of care ultrasound; simulation; simulation based medical education; ultrasound protocol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



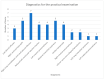
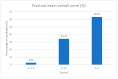
References
-
- Robba C., Wong A., Poole D., Al Tayar A., Arntfield R.T., Chew M.S., Corradi F., Douflé G., Goffi A., Lamperti M., et al. Basic ultrasound head-to-toe skills for intensivists in the general and neuro intensive care unit population: Consensus and expert recommendations of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 2021;47:1347–1367. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06486-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Volpicelli G., Elbarbary M., Blaivas M., Lichtenstein D.A., Mathis G., Kirkpatrick A.W., Melniker L., Gargani L., Noble V.E., Via G., et al. International Liaison Committee on Lung Ultrasound (ILC-LUS) for International Consensus Conference on Lung Ultrasound (ICC-LUS). International evidence-based recommendations for point-of-care lung ultrasound. Intensive Care Med. 2012;38:577–591. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2513-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cecconi M., De Backer D., Antonelli M., Beale R., Bakker J., Hofer C., Jaeschke R., Mebazaa A., Pinsky M.R., Teboul J.L., et al. Consensus on circulatory shock and hemodynamic monitoring. Task force of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 2014;40:1795–1815. doi: 10.1007/s00134-014-3525-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

