An Informative Review of Radiomics Studies on Cancer Imaging: The Main Findings, Challenges and Limitations of the Methodologies
- PMID: 38248112
- PMCID: PMC10814313
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol31010027
An Informative Review of Radiomics Studies on Cancer Imaging: The Main Findings, Challenges and Limitations of the Methodologies
Abstract
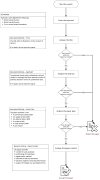
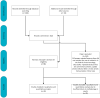
The aim of this informative review was to investigate the application of radiomics in cancer imaging and to summarize the results of recent studies to support oncological imaging with particular attention to breast cancer, rectal cancer and primitive and secondary liver cancer. This review also aims to provide the main findings, challenges and limitations of the current methodologies. Clinical studies published in the last four years (2019-2022) were included in this review. Among the 19 studies analyzed, none assessed the differences between scanners and vendor-dependent characteristics, collected images of individuals at additional points in time, performed calibration statistics, represented a prospective study performed and registered in a study database, conducted a cost-effectiveness analysis, reported on the cost-effectiveness of the clinical application, or performed multivariable analysis with also non-radiomics features. Seven studies reached a high radiomic quality score (RQS), and seventeen earned additional points by using validation steps considering two datasets from two distinct institutes and open science and data domains (radiomics features calculated on a set of representative ROIs are open source). The potential of radiomics is increasingly establishing itself, even if there are still several aspects to be evaluated before the passage of radiomics into routine clinical practice. There are several challenges, including the need for standardization across all stages of the workflow and the potential for cross-site validation using real-world heterogeneous datasets. Moreover, multiple centers and prospective radiomics studies with more samples that add inter-scanner differences and vendor-dependent characteristics will be needed in the future, as well as the collecting of images of individuals at additional time points, the reporting of calibration statistics and the performing of prospective studies registered in a study database.
Keywords: biomedical imaging; deep learning; machine learning; radiomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The application of radiomics in cancer imaging with a focus on lung cancer, renal cell carcinoma, gastrointestinal cancer, and head and neck cancer: A systematic review.Phys Med. 2025 Feb;130:104891. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2025.104891. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Phys Med. 2025. PMID: 39787678
-
Current progress and quality of radiomic studies for predicting EGFR mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer using PET/CT images: a systematic review.Br J Radiol. 2021 Jun 1;94(1122):20201272. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20201272. Epub 2021 May 12. Br J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33882244 Free PMC article.
-
"Real-world" radiomics from multi-vendor MRI: an original retrospective study on the prediction of nodal status and disease survival in breast cancer, as an exemplar to promote discussion of the wider issues.Cancer Imaging. 2021 May 20;21(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s40644-021-00406-6. Cancer Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34016188 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of science and reporting for radiomics in cardiac magnetic resonance imaging studies: a systematic review.Eur Radiol. 2022 Jul;32(7):4361-4373. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08587-9. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35230519
-
The quality and clinical translation of radiomics studies based on MRI for predicting Ki-67 levels in patients with breast cancer.Br J Radiol. 2023 Oct;96(1150):20230172. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20230172. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Br J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37724784 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Predictive Role of Radiomics in Breast Cancer Patients Imaged by [18F]FDG PET: Preliminary Results from a Prospective Cohort.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Oct 17;14(20):2312. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14202312. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451637 Free PMC article.
-
Treatments and cancer: implications for radiologists.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 16;16:1564909. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1564909. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40308594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiomics in radiology: What the radiologist needs to know about technical aspects and clinical impact.Radiol Med. 2024 Dec;129(12):1751-1765. doi: 10.1007/s11547-024-01904-w. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Radiol Med. 2024. PMID: 39472389 Review.
-
Predictive value of MRI-based deep learning model for lymphovascular invasion status in node-negative invasive breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 13;14(1):16204. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67217-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39003325 Free PMC article.
-
A novel MRI-based radiomics for preoperative prediction of lymphovascular invasion in rectal cancer.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Aug;50(8):3377-3390. doi: 10.1007/s00261-025-04800-7. Epub 2025 Jan 12. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39799548
References
-
- Lambin P., Leijenaar R.T.H., Deist T.M., Peerlings J., de Jong E.E.C., van Timmeren J., Sanduleanu S., Larue R.T.H.M., Even A.J.G., Jochems A., et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017;14:749–762. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.141. - DOI - PubMed
-
- He X., Li K., Wei R., Zuo M., Yao W., Zheng Z., He X., Fu Y., Li C., An C., et al. A multitask deep learning radiomics model for predicting the macrotrabecular-massive subtype and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. Radiol. Med. 2023;128:1508–1520. doi: 10.1007/s11547-023-01719-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical