Probabilistic Nearest Neighbors Classification
- PMID: 38248165
- PMCID: PMC10814015
- DOI: 10.3390/e26010039
Probabilistic Nearest Neighbors Classification
Abstract
Analysis of the currently established Bayesian nearest neighbors classification model points to a connection between the computation of its normalizing constant and issues of NP-completeness. An alternative predictive model constructed by aggregating the predictive distributions of simpler nonlocal models is proposed, and analytic expressions for the normalizing constants of these nonlocal models are derived, ensuring polynomial time computation without approximations. Experiments with synthetic and real datasets showcase the predictive performance of the proposed predictive model.
Keywords: NP-completeness; nearest neighbors classification; probabilistic machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

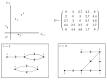


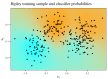

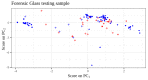
References
-
- Fix E., Hodges J.L. Discriminatory analysis—Nonparametric discrimination: Consistency properties. Int. Stat. Rev. 1989;57:238–247. doi: 10.2307/1403797. - DOI
-
- Devroye L., Györfi L., Lugosi G. A Probabilistic Theory of Pattern Recognition. Volume 31 Springer; Berlin, Germany: 2013.
-
- Biau G., Devroye L. Lectures on the Nearest Neighbor Method. Volume 246 Springer; Berlin, Germany: 2015.
-
- Holmes C., Adams N. A probabilistic nearest neighbour method for statistical pattern recognition. J. R. Stat. Soc. B Stat. Methodol. 2002;64:295–306. doi: 10.1111/1467-9868.00338. - DOI
-
- Cucala L., Marin J.M., Robert C.P., Titterington D.M. A Bayesian Reassessment of Nearest-Neighbor Classification. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2009;104:263–273. doi: 10.1198/jasa.2009.0125. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

