Automation in Dentistry with Mechanical Drills and Lasers for Implant Osteotomy: A Narrative-Scoping Review
- PMID: 38248216
- PMCID: PMC10814723
- DOI: 10.3390/dj12010008
Automation in Dentistry with Mechanical Drills and Lasers for Implant Osteotomy: A Narrative-Scoping Review
Abstract
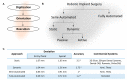
The popularity of implants is increasing with the aging population requiring oral-dental rehabilitation. There are several critical steps in the implant workflow, including case selection, implant design, surgical procedure, biological tissue responses, and functional restoration. Among these steps, surgical osteotomy procedures are a crucial determinant of clinical success. This brief review was aimed at outlining the current state of the field in automation-assisted implant surgical osteotomy technologies. A broad search of the literature was performed to identify current literature. The results are outlined in three broad categories: semi-automated static (image-guided) or dynamic (navigation-assisted) systems, and fully-automated robotic systems. As well as the current mechanical rotary approaches, the literature supporting the use of lasers in further refinement of these approaches is reviewed. The advantages and limitations of adopting autonomous technologies in practical clinical dental practices are discussed. In summary, advances in clinical technologies enable improved precision and efficacious clinical outcomes with implant dentistry. Hard-tissue lasers offer further advancements in precision, improved biological responses, and favorable clinical outcomes that require further investigation.
Keywords: automation; implants; lasers; osteotomy; robotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Guided innovations: Robot-assisted dental implant surgery.J Prosthet Dent. 2022 May;127(5):673-674. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2022.03.029. Epub 2022 May 26. J Prosthet Dent. 2022. PMID: 35643826
-
Digital Workflow and Guided Surgery in Implant Therapy-Literature Review and Practical Tips to Optimize Precision.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2025 Jun;27(3):e70038. doi: 10.1111/cid.70038. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 40304451 Review.
-
Accuracy and Precision of Haptic Robotic-Guided Implant Surgery in a Large Consecutive Series.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2024 Feb 27;39(1):99-106. doi: 10.11607/jomi.10468. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2024. PMID: 37939239
-
Three-dimensional navigation in implant dentistry.Eur J Esthet Dent. 2007 Spring;2(1):80-98. Eur J Esthet Dent. 2007. PMID: 19655496
-
Heat generated by dental implant drills during osteotomy-a review: heat generated by dental implant drills.J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2014 Jun;14(2):131-43. doi: 10.1007/s13191-014-0350-6. Epub 2014 Feb 18. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2014. PMID: 24757349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Application of machine learning in dentistry: insights, prospects and challenges.Acta Odontol Scand. 2025 Mar 27;84:145-154. doi: 10.2340/aos.v84.43345. Acta Odontol Scand. 2025. PMID: 40145687 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aiquel L.L., Pitta J., Antonoglou G.N., Mischak I., Sailer I., Payer M. Does the timing of implant placement and loading influence biological outcomes of implant-supported multiple-unit fixed dental prosthesis-A systematic review with meta-analyses. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2021;32((Suppl. S21)):5–27. doi: 10.1111/clr.13860. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

