Brain Health and Cognition in Older Adults: Roadmap and Milestones towards the Implementation of Preventive Strategies
- PMID: 38248270
- PMCID: PMC10813413
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci14010055
Brain Health and Cognition in Older Adults: Roadmap and Milestones towards the Implementation of Preventive Strategies
Abstract
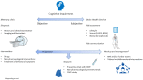
In this narrative review, we delve into the evolving concept of brain health, as recognized by the WHO, focusing on its intersection with cognitive decline. We emphasize the imperative need for preventive strategies, particularly in older adults. We describe the target population that might benefit the most from risk-based approaches-namely, people with subjective cognitive decline. Additionally, we consider universal prevention in cognitively unimpaired middle-aged and older adults. Delving into multidomain personalized preventive strategies, we report on empirical evidence surrounding modifiable risk factors and interventions crucial in mitigating cognitive decline. Next, we highlight the emergence of brain health services (BHS). We explain their proposed role in risk assessment, risk communication, and tailored interventions to reduce the risk of dementia. Commenting on ongoing BHS pilot experiences, we present the inception and framework of our own BHS in Monza, Italy, outlining its operational structure and care pathways. We emphasize the need for global collaboration and intensified research efforts to address the intricate determinants of brain health and their potential impact on healthcare systems worldwide.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; brain health; cognition; prevention; subjective cognitive decline.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Optimizing Brain Health across the Life Course. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2022.
-
- Simons R.L., Ong M.L., Beach S.R.H., Lei M.K., Philibert R., Mielke M.M. Direct and indirect effects of socioeconomic status and discrimination on subjective cognitive decline: A longitudinal study of African American women. J. Gerontol. B. Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2023;78:799–808. doi: 10.1093/geronb/gbad029. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Borelli W.V., Zimmer E.R., Bieger A., Coelho B., Pascoal T.A., Chaves M.L.F., Amariglio R., Castilhos R.M. Subjective cognitive decline in Brazil: Prevalence and association with dementia modifiable risk factors in a population-based study. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2022;14:e12368. doi: 10.1002/dad2.12368. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

