An Angular Acceleration Based Looming Detector for Moving UAVs
- PMID: 38248596
- PMCID: PMC11154257
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics9010022
An Angular Acceleration Based Looming Detector for Moving UAVs
Abstract
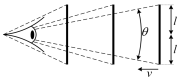
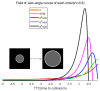
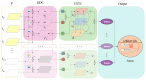
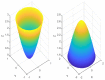
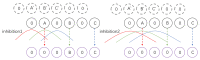
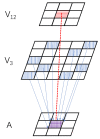
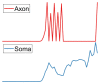
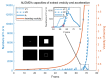
Visual perception equips unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) with increasingly comprehensive and instant environmental perception, rendering it a crucial technology in intelligent UAV obstacle avoidance. However, the rapid movements of UAVs cause significant changes in the field of view, affecting the algorithms' ability to extract the visual features of collisions accurately. As a result, algorithms suffer from a high rate of false alarms and a delay in warning time. During the study of visual field angle curves of different orders, it was found that the peak times of the curves of higher-order information on the angular size of looming objects are linearly related to the time to collision (TTC) and occur before collisions. This discovery implies that encoding higher-order information on the angular size could resolve the issue of response lag. Furthermore, the fact that the image of a looming object adjusts to meet several looming visual cues compared to the background interference implies that integrating various field-of-view characteristics will likely enhance the model's resistance to motion interference. Therefore, this paper presents a concise A-LGMD model for detecting looming objects. The model is based on image angular acceleration and addresses problems related to imprecise feature extraction and insufficient time series modeling to enhance the model's ability to rapidly and precisely detect looming objects during the rapid self-motion of UAVs. The model draws inspiration from the lobula giant movement detector (LGMD), which shows high sensitivity to acceleration information. In the proposed model, higher-order information on the angular size is abstracted by the network and fused with multiple visual field angle characteristics to promote the selective response to looming objects. Experiments carried out on synthetic and real-world datasets reveal that the model can efficiently detect the angular acceleration of an image, filter out insignificant background motion, and provide early warnings. These findings indicate that the model could have significant potential in embedded collision detection systems of micro or small UAVs.
Keywords: Bio-inspired Neural Networks; LGMD; UAV; collision detection; dynamic vision.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships.
Figures
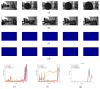

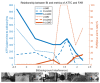
References
-
- Bachrach A., He R., Roy N. Autonomous flight in unknown indoor environments. Int. J. Micro Air Veh. 2009;1:217–228. doi: 10.1260/175682909790291492. - DOI
-
- Xiang Y., Zhang Y. Sense and avoid technologies with applications to unmanned aircraft systems: Review and prospects. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2015;74:152–166.
-
- Temizer I., Donovan J.C., Baier H., Semmelhack J.L. A Visual Pathway for Looming-Evoked Escape in Larval Zebrafish. Curr. Biol. 2015;25:1823–1834. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

