Common infections and neuroimaging markers of dementia in three UK cohort studies
- PMID: 38248636
- PMCID: PMC10984486
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.13613
Common infections and neuroimaging markers of dementia in three UK cohort studies
Abstract
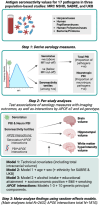
Introduction: We aimed to investigate associations between common infections and neuroimaging markers of dementia risk (brain volume, hippocampal volume, white matter lesions) across three population-based studies.
Methods: We tested associations between serology measures (pathogen serostatus, cumulative burden, continuous antibody responses) and outcomes using linear regression, including adjustments for total intracranial volume and scanner/clinic information (basic model), age, sex, ethnicity, education, socioeconomic position, alcohol, body mass index, and smoking (fully adjusted model). Interactions between serology measures and apolipoprotein E (APOE) genotype were tested. Findings were meta-analyzed across cohorts (Nmain = 2632; NAPOE-interaction = 1810).
Results: Seropositivity to John Cunningham virus associated with smaller brain volumes in basic models (β = -3.89 mL [-5.81, -1.97], Padjusted < 0.05); these were largely attenuated in fully adjusted models (β = -1.59 mL [-3.55, 0.36], P = 0.11). No other relationships were robust to multiple testing corrections and sensitivity analyses, but several suggestive associations were observed.
Discussion: We did not find clear evidence for relationships between common infections and markers of dementia risk. Some suggestive findings warrant testing for replication.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; cerebral small vessel disease; common infections; dementia; multiplex serology; pathogen burden.
© 2024 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
J.M.S. has received research funding and PET tracers from AVID Radiopharmaceuticals (a wholly owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly) and Alliance Medical; has consulted for Roche, Eli Lilly, Biogen, AVID, Merck, and GE; and received royalties from Oxford University Press and Henry Stewart Talks. He is Chief Medical Officer for Alzheimer's Research UK. N.C. receives funds from AstraZeneca for serving on data safety and monitoring committees for clinical trials of glucose lowering agents. R.E.G., C.H.S., C.W.G., J.B., T.W., A.D.H., M.R., D.M.W. report no competing interests. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Alcohol Consumption, Brain Amyloid-β Deposition, and Brain Structural Integrity Among Older Adults Free of Dementia.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;74(2):509-519. doi: 10.3233/JAD-190834. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 32039843 Free PMC article.
-
"Life's Essential 8" Cardiovascular Health and Dementia Risk, Cognition, and Neuroimaging Markers of Brain Health.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2023 Nov;24(11):1791-1797. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2023.05.023. Epub 2023 Jun 24. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2023. PMID: 37369360
-
APOE-related risk of mild cognitive impairment and dementia for prevention trials: An analysis of four cohorts.PLoS Med. 2017 Mar 21;14(3):e1002254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002254. eCollection 2017 Mar. PLoS Med. 2017. PMID: 28323826 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy, subcortical white matter disease and dementia: literature review and study in OPTIMA.Brain Pathol. 2015 Jan;25(1):51-62. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12221. Brain Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25521177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex differences in functional and molecular neuroimaging biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease in cognitively normal older adults with subjective memory complaints.Alzheimers Dement. 2018 Sep;14(9):1204-1215. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.05.014. Epub 2018 Jul 7. Alzheimers Dement. 2018. PMID: 30201102 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic signatures of corona and herpes viral antibodies identify IGDCC4 as a mediator of neurodegeneration.Sci Adv. 2025 May 30;11(22):eadt7176. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adt7176. Epub 2025 May 30. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40446030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lotz SK, Blackhurst BM, Reagin KL, Funk KE. Microbial infections are a risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15:691136. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fncel.2021.691136 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

