Marine Bioprospecting: Enzymes and Stress Proteins from the Sea Anemones Anthopleura dowii and Lebrunia neglecta
- PMID: 38248637
- PMCID: PMC10821040
- DOI: 10.3390/md22010012
Marine Bioprospecting: Enzymes and Stress Proteins from the Sea Anemones Anthopleura dowii and Lebrunia neglecta
Abstract
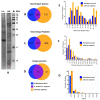
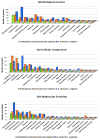
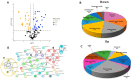
The bioprospecting of sea anemone tissues and secretions has revealed that they are natural libraries of polypeptides with diverse biological activities that can be utilized to develop of biotechnological tools with potential medical and industrial applications. This study conducted a proteomic analysis of crude venom extracts from Anthopleura dowii Verrill, 1869, and Lebrunia neglecta Duchassaing & Michelotti, 1860. The obtained data allowed us to identify 201 polypeptides, of which 39% were present in both extracts. Among the obtained sequences, hydrolase-type enzymes, oxidoreductases, transferases, heat shock proteins, adhesion proteins, and protease inhibitors, among others, were identified. Interaction analysis and functional annotation indicated that these proteins are primarily involved in endoplasmic reticulum metabolic processes such as carbon metabolism and protein processing. In addition, several proteins related to oxidative stress were identified, including superoxide dismutase, peroxiredoxins, thioredoxin, and glutathione oxidase. Our results provide novel information on the polypeptide composition of the crude venom extract from sea anemones, which can be utilized to develop molecules for therapeutic tools and industrial applications.
Keywords: Anthopleura dowii; Lebrunia neglecta; crude venom extract; enzymes; proteome; sea anemone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest in relation to the publication of this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analysis of the Tentacles and Mucus of Anthopleura dowii Verrill, 1869.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jul 25;17(8):436. doi: 10.3390/md17080436. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31349621 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing and de novo transcriptome assembly of Anthopleura dowii Verrill (1869), from Mexico.Genom Data. 2016 Dec 5;11:92-94. doi: 10.1016/j.gdata.2016.11.022. eCollection 2017 Mar. Genom Data. 2016. PMID: 28066713 Free PMC article.
-
A Sea Anemone Lebrunia neglecta Venom Fraction Decreases Boar Sperm Cells Capacitation: Possible Involvement of HVA Calcium Channels.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Apr 7;14(4):261. doi: 10.3390/toxins14040261. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35448870 Free PMC article.
-
Sea anemone venom: Ecological interactions and bioactive potential.Toxicon. 2022 Mar;208:31-46. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2022.01.004. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Toxicon. 2022. PMID: 35065159 Review.
-
Discovery of novel peptide neurotoxins from sea anemone species.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2021 Nov 30;26(11):1256-1273. doi: 10.52586/5022. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2021. PMID: 34856766 Review.
Cited by
-
Large-Scale AI-Based Structure and Activity Prediction Analysis of ShK Domain Peptides from Sea Anemones in the South China Sea.Mar Drugs. 2025 Feb 16;23(2):85. doi: 10.3390/md23020085. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39997209 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Debashish G., Malay S., Barindra S., Joydeep M. Marine Enzymes. In: Ulber R., Le Gal Y., editors. Marine Biotechnology I. Volume 96. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2005. pp. 189–218. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology.
-
- Bekiari M. Marine Bioprospecting: Understanding the Activity and Some Challenges Related to Environmental Protection, Scientific Research, Ethics, and the Law. In: da Gloria Garcia M., Cortês A., editors. Blue Planet Law: The Ecology of Our Economic and Technological World. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2023. pp. 237–252. (Sustainable Development Goals Series).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

