New l-Rhamnose-Binding Lectin from the Bivalve Glycymeris yessoensis: Purification, Partial Structural Characterization and Antibacterial Activity
- PMID: 38248652
- PMCID: PMC10817417
- DOI: 10.3390/md22010027
New l-Rhamnose-Binding Lectin from the Bivalve Glycymeris yessoensis: Purification, Partial Structural Characterization and Antibacterial Activity
Abstract
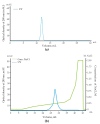
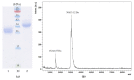
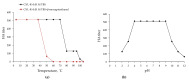
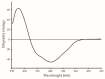
In this study, a new l-rhamnose-binding lectin (GYL-R) from the hemolymph of bivalve Glycymeris yessoensis was purified using affinity and ion-exchange chromatography and functionally characterized. Lectin antimicrobial activity was examined in different ways. The lectin was inhibited by saccharides possessing the same configuration of hydroxyl groups at C-2 and C-4, such as l-rhamnose, d-galactose, lactose, l-arabinose and raffinose. Using the glycan microarray approach, natural carbohydrate ligands were established for GYL-R as l-Rha and glycans containing the α-Gal residue in the terminal position. The GYL-R molecular mass determined by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry was 30,415 Da. The hemagglutination activity of the lectin was not affected by metal ions. The lectin was stable up to 75 °C and between pH 4.0 and 12.0. The amino acid sequence of the five GYL-R segments was obtained with nano-ESI MS/MS and contained both YGR and DPC-peptide motifs which are conserved in most of the l-rhamnose-binding lectin carbohydrate recognition domains. Circular dichroism confirmed that GYL is a α/β-protein with a predominance of the random coil. Furthermore, GYL-R was able to bind and suppress the growth of the Gram-negative bacteria E. coli by recognizing lipopolysaccharides. Together, these results suggest that GYL-R is a new member of the RBL family which participates in the self-defense mechanism against bacteria and pathogens with a distinct carbohydrate-binding specificity.
Keywords: bivalve lectin; hemolymph; innate immune; l-rhamnose-binding lectin; microorganism binding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

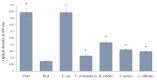
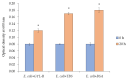
References
-
- Ahmmed M.K., Bhowmik S., Giteru S.G., Zilani M.N.H., Adadi P., Islam S.S., Kanwugu O.N., Haq M., Ahmmed F., Ng C.C.W., et al. An Update of Lectins from Marine Organisms: Characterization, Extraction Methodology, and Potential Biofunctional Applications. Mar. Drugs. 2022;20:430. doi: 10.3390/md20070430. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

